Page 72 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 72
P1: GQT/LBX P2: GQT/MBQ QC: FYD Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN008C-602 July 25, 2001 20:31
Macromolecules, Structure 887
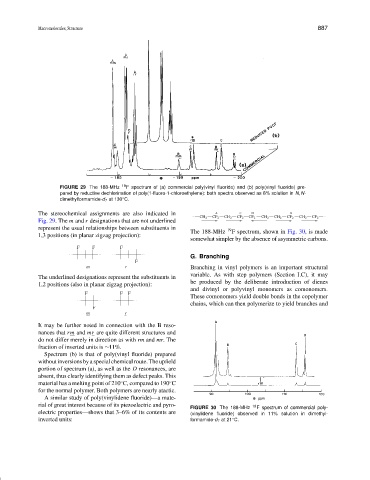
FIGURE 29 The 188-MHz 19 F spectrum of (a) commercial poly(vinyl fluoride) and (b) poly(vinyl fluoride) pre-
pared by reductive dechlorination of poly(1-fluoro-1-chloroethylene): both spectra observed as 8% solution in N,N-
◦
dimethylformamide-d 7 at 130 C.
The stereochemical assignments are also indicated in A C D B
CH 2 CF 2 CH 2 CF 2 CF 2 CH 2 CH 2 CF 2 CH 2 CF 2
Fig. 29. The m and r designations that are not underlined
represent the usual relationships between substituents in 19
The 188-MHz F spectrum, shown in Fig. 30, is made
1,3 positions (in planar zigzag projection):
somewhat simpler by the absence of asymmetric carbons.
F F F
G. Branching
F
m r Branching in vinyl polymers is an important structural
variable. As with step polymers (Section I.C), it may
The underlined designations represent the substituents in
be produced by the deliberate introduction of dienes
1,2 positions (also in planar zigzag projection):
and divinyl or polyvinyl monomers as comonomers.
F F F
These comonomers yield double bonds in the copolymer
chains, which can then polymerize to yield branches and
F
m r
It may be further noted in connection with the B reso-
nances that rm and mr are quite different structures and
do not differ merely in direction as with rm and mr. The
fraction of inverted units is ∼11%.
Spectrum (b) is that of poly(vinyl fluoride) prepared
without inversions by a special chemical route. The upfield
portion of spectrum (a), as well as the D resonances, are
absent, thus clearly identifying them as defect peaks. This
material has a melting point of 210 C, compared to 190 C
◦
◦
for the normal polymer. Both polymers are nearly atactic.
A similar study of poly(vinylidene fluoride)—a mate-
rial of great interest because of its piezoelectric and pyro- 19
FIGURE 30 The 188-MHz F spectrum of commercial poly-
electric properties—shows that 3–6% of its contents are (vinylidene fluoride) observed in 11% solution in dimethyl-
inverted units: formamide-d 7 at 21 C.
◦