Page 78 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 78
P1: GQT/LBX P2: GQT/MBQ QC: FYD Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN008C-602 July 25, 2001 20:31
Macromolecules, Structure 893
the conformational changes that occur in heme-proteins
upon binding small molecules.
Fluorescence measurements have long been used to
study the conformations of biopolymers. Phenylalanine,
tyrosine, and typtophan fluoresce. Because solvents affect
the fluorescence intensity of proteins, solvent studies can,
in favorable cases, be used to establish the hydrophobicity
of the environment surrounding these residues. Fluores-
cent dyes, or fluorescence probes, can be attached to or
entrained in biological molecules to provide additional
conformationally sensitive information.
Excimerformationstudiesareveryusefulinprobingthe
conformations of synthetic polymers in solution. An ex-
cimer is an association complex between an excited chro-
mophore and a chromophore in the ground state. The ex-
cimer emission band is shifted toward longer wavelengths
than normally would be observed. Efficient formation of
excimer complexes depends on spatial proximity of the
chromophores, which can thus be used to establish con-
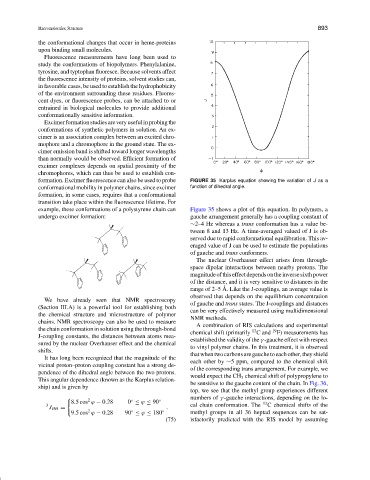
formation. Excimer fluorescence can also be used to probe FIGURE 35 Karplus equation showing the variation of J as a
conformational mobility in polymer chains, since excimer function of dihedral angle.
formation, in some cases, requires that a conformational
transition take place within the fluorescence lifetime. For
example, these conformations of a polystyrene chain can Figure 35 shows a plot of this equation. In polymers, a
undergo excimer formation: gauche arrangement generally has a coupling constant of
∼2–4 Hz whereas a trans conformation has a value be-
tween 8 and 13 Hz. A time-averaged valued of J is ob-
served due to rapid conformational equilibration. This av-
eraged value of J can be used to estimate the populations
of gauche and trans conformers.
The nuclear Overhauser effect arises from through-
space dipolar interactions between nearby protons. The
magnitudeofthiseffectdependsontheinversesixthpower
of the distance, and it is very sensitive to distances in the
˚
range of 2–5 A. Like the J-couplings, an average value is
observed that depends on the equilibrium concentration
We have already seen that NMR spectroscopy
of gauche and trans states. The J-couplings and distances
(Section III.A) is a powerful tool for establishing both
can be very effectively measured using multidimensional
the chemical structure and microstructure of polymer
NMR methods.
chains. NMR spectroscopy can also be used to measure
A combination of RIS calculations and experimental
the chain conformation in solution using the through-bond 13 19
chemical shift (primarily C and F) measurements has
J-coupling constants, the distances between atoms mea-
established the validity of the γ -gauche effect with respect
sured by the nuclear Overhauser effect and the chemical
to vinyl polymer chains. In this treatment, it is observed
shifts.
that when two carbons are gauche to each other, they shield
It has long been recognized that the magnitude of the
each other by ∼5 ppm, compared to the chemical shift
vicinal proton–proton coupling constant has a strong de-
of the corresponding trans arrangement. For example, we
pendence of the dihedral angle between the two protons.
would expect the CH 3 chemical shift of polypropylene to
This angular dependence (known as the Karplus relation-
be sensitive to the gauche content of the chain. In Fig. 36,
ship) and is given by
top, we see that the methyl group experiences different
numbers of γ -gauche interactions, depending on the lo-
2
◦
8.5 cos ϕ − 0.28 0 ≤ ϕ ≤ 90 ◦ 13
3 cal chain conformation. The C chemical shifts of the
J HH = .
2
◦
9.5 cos ϕ − 0.28 90 ≤ ϕ ≤ 180 ◦ methyl groups in all 36 heptad sequences can be sat-
(75) isfactorily predicted with the RIS model by assuming