Page 280 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 280
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009M-428 July 18, 2001 1:6
Metal Particles and Cluster Compounds 537
a multicenter bonding model would seem much more ap- pounds due to the closed-cage type structure of the clus-
propriate for cluster compounds. The polyhedral skeletal ter skeleton. Each B H unit has four valence electrons.
electron pair (PSEP) theory developed by Wade is one Of these four electrons two are needed for a B H bond
such model. This bonding model was developed to ex- leaving two electrons which are available for the bonding
plain boron cluster compounds but has been successfully needs of the cluster skeleton. A cluster with this general
extended to transition-metal cluster compounds. Perhaps formula will therefore have n + 1 electron pairs for clus-
the PSEP theory would best be understood by first seeing ter bonding (one pair from each BH unit and one pair
how it applies to the borane systems for which is was de- from the overall charge on the complex). In general, com-
veloped, keeping in mind the method also works for metal pounds with n + 1 electron pairs are found to have closo
cluster compounds. geometries.
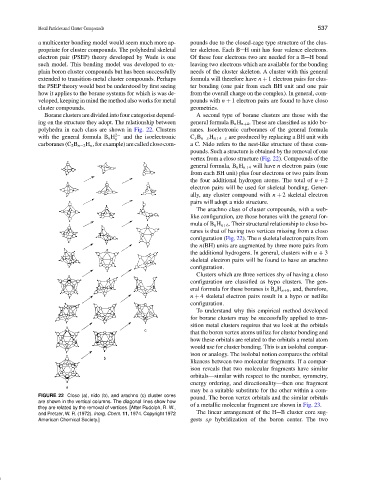
Borane clusters are divided into four categorise depend- A second type of borane clusters are those with the
ing on the structure they adopt. The relationship between general formula B n H n +4 . These are classified as nido bo-
polyhedra in each class are shown in Fig. 22. Clusters ranes. Isoelectronic carboranes of the general formula
with the general formula B n H 2− and the isoelectronic C x B n −x H n +4−x are produced by replacing a BH unit with
n
carboranes(C 2 B n −2 H n ,forexample)arecalledclosocom- a C. Nido refers to the nest-like structure of these com-
pounds. Such a structure is obtained by the removal of one
vertex from a closo structure (Fig. 22). Compounds of the
general formula, B n H n +4 will have n electron pairs (one
from each BH unit) plus four electrons or two pairs from
the four additional hydrogen atoms. The total of n + 2
electron pairs will be used for skeletal bonding. Gener-
ally, any cluster compound with n + 2 skeletal electron
pairs will adopt a nido structure.
The arachno class of cluster compounds, with a web-
like configuration, are those boranes with the general for-
mula of B n H n +6 . Their structural relationship to closo bo-
ranes is that of having two vertices missing from a closo
configuration (Fig. 22). The n skeletal electron pairs from
the n(BH) units are augmented by three more pairs from
the additional hydrogens. In general, clusters with n + 3
skeletal electron pairs will be found to have an arachno
configuration.
Clusters which are three vertices shy of having a closo
configuration are classified as hypo clusters. The gen-
eral formula for these boranes is B n H n +8 , and, therefore,
n + 4 skeletal electron pairs result in a hypo or netlike
configuration.
To understand why this empirical method developed
for borane clusters may be successfully applied to tran-
sition metal clusters requires that we look at the orbitals
that the boron vertex atoms utilize for cluster bonding and
how these orbitals are related to the orbitals a metal atom
would use for cluster bonding. This is an isolobal compar-
ison or analogy. The isolobal notion compares the orbital
likeness between two molecular fragments. If a compar-
ison reveals that two molecular fragments have similar
orbitals—similar with respect to the number, symmetry,
energy ordering, and directionality—then one fragment
may be a suitable substitute for the other within a com-
FIGURE 22 Closo (a), nido (b), and arachno (c) cluster cores pound. The boron vertex orbitals and the similar orbitals
are shown in the vertical columns. The diagonal lines show how
they are related by the removal of vertices. [After Rudolph, R. W., of a metallic molecular fragment are shown in Fig. 23.
and Pretzer, W. R. (1972). Inorg. Chem. 11, 1974. Copyright 1972 The linear arrangement of the H B cluster core sug-
American Chemical Society.] gests sp hybridization of the boron center. The two