Page 319 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 319
P1: GPA Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN010b-481 July 14, 2001 18:45
Noble Metals (Chemistry) 473
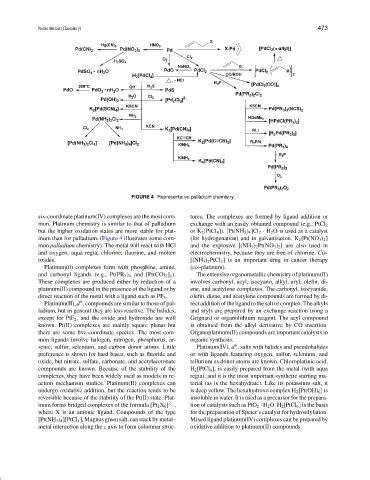
FIGURE 4 Representative palladium chemistry.
six-coordinate platinum(IV) complexes are the most com- tures. The complexes are formed by ligand addition or
mon. Platinum chemistry is similar to that of palladium exchange with an easily obtained compound (e.g., PtCl 2
but the higher oxidation states are more stable for plat- or K 2 [PtCl 4 ]). [Pt(NH 3 ) 4 ]Cl 2 · H 2 O is used as a catalyst
inum than for palladium. (Figure 4 illustrates some com- (for hydrogenation) and in galvanization. K 2 [Pt(NO 3 ) 4 ]
mon palladium chemistry). The metal will react with HCl and the explosive [(NH 3 ) 2 Pt(NO 3 ) 2 ] are also used in
and oxygen, aqua regia, chlorine, fluorine, and molten electrochemistry, because they are free of chlorine. Cis-
oxides. [(NH 3 ) 2 PtCl 2 ] is an important drug in cancer therapy
Platinum(0) complexes form with phosphine, amine, (cis-platinum).
and carbonyl ligands (e.g., Pt(PR 3 ) 4 and [Pt(CO) 2 ] n ). The extensive organometallic chemistry of platinum(II)
These complexes are produced either by reduction of a involves carbonyl, acyl, isocyano, alkyl, aryl, olefin, di-
platinum(II) compound in the presence of the ligand or by ene, and acetylene complexes. The carbonyl, isocyanide,
direct reaction of the metal with a ligand such as PF 3 . olefin, diene, and acetylene compounds are formed by di-
8
Platinum(II), d , compounds are similar to those of pal- rectadditionoftheligandtothesaltorcomplex.Thealkyls
ladium, but in general they are less reactive. The halides, and aryls are prepared by an exchange reaction using a
except for PtF 2 , and the oxide and hydroxide are well Grignard or organolithium reagent. The acyl compound
known. Pt(II) complexes are mainly square planar but is obtained from the alkyl derivative by CO insertion.
there are some five-coordinate species. The most com- Organoplatinum(II) compounds are important catalysts in
mon ligands involve halogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, ar- organic synthesis.
6
senic, sulfur, selenium, and carbon donor atoms. Little Platinum(IV), d , salts with halides and pseudohalides
preference is shown for hard bases, such as fluoride and or with ligands featuring oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and
oxide, but nitrate, sulfate, carbonate, and acetylacetonate tellurium as donor atoms are known. Chloroplatinic acid,
compounds are known. Because of the stability of the H 2 [PtCl 6 ], is easily prepared from the metal (with aqua
complexes, they have been widely used as models in re- regia), and it is the most important synthetic starting ma-
action mechanism studies. Platinum(II) complexes can terial (as is the hexahydrate). Like its potassium salt, it
undergo oxidative addition, but the reaction tends to be is deep yellow. The hexahydroxo complex H 2 [Pt(OH) 6 ]is
reversible because of the stability of the Pt(II) state. Plat- insoluble in water. It is used as a precursor for the prepara-
inum forms bridged complexes of the formula [Pt 2 X 6 ] , tion of catalysts such as PtO 2 · H 2 O. H 2 [PtCl 6 ] is the basis
2−
where X is an anionic ligand. Compounds of the type for the preparation of Speier’s catalyst for hydrosilylation.
[Pt(NH 3 ) 4 ][PtCl 4 ], Magnus greensalt, can stack by metal– Mixed ligand platinum(IV) complexes can be prepared by
metal interaction along the z axis to form columnar struc- oxidative addition to platinum(II) compounds.