Page 101 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 101
P1: GTQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017F-788 August 3, 2001 16:27
42 Translation of RNA to Protein
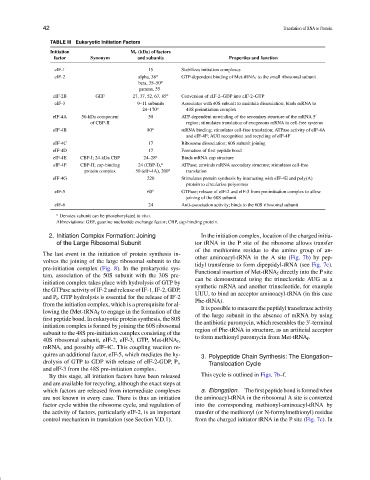
TABLE III Eukaryotic Initiation Factors
Initiation M r (kDa) of factors
factor Synonym and subunits Properties and function
eIF-1 15 Stabilizes initiation complexes
eIF-2 alpha, 38 a GTP-dependent binding of Met-tRNA f to the small ribosomal subunit
beta, 35–50 a
gamma, 55
eIF-2B GEF 27, 37, 52, 67, 85 a Conversion of eIF-2–GDP into eIF-2–GTP
eIF-3 9–11 subunits Associates with 40S subunit to maintain dissociation; binds mRNA to
24–170 a 43S preinitiation complex
eIF-4A 50-kDa component 50 ATP-dependent unwinding of the secondary structure of the mRNA 5
of CBP-II region; stimulates translation of exogenous mRNA in cell-free systems
eIF-4B 80 a mRNA binding; stimulates cell-free translation; ATPase activity of eIF-4A
and eIF-4F; AUG recognition and recycling of eIF-4F
eIF-4C 17 Ribosome dissociation; 60S subunit joining
eIF-4D 17 Formation of first peptide bond
eIF-4E CBP-I; 24-kDa CBP 24–28 a Binds mRNA cap structure
eIF-4F CBP-II; cap-binding 24 (CBP-I), a ATPase; unwinds mRNA secondary structure; stimulates cell-free
protein complex 50 (eIF-4A), 200 a translation
eIF-4G 220 Stimulates protein synthesis by interacting with eIF-4E and poly(A)
protein to circularize polysomes
eIF-5 60 a GTPase; release of eIF-2 and eIF-3 from pre-initiation complex to allow
joining of the 60S subunit
eIF-6 24 Anti-association activity; binds to the 60S ribosomal subunit
a Denotes subunit can be phosphorylated in vivo.
Abbreviations: GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; CBP, cap-binding protein.
2. Initiation Complex Formation: Joining In the initiation complex, location of the charged initia-
of the Large Ribosomal Subunit tor tRNA in the P site of the ribosome allows transfer
of the methionine residue to the amino group of an-
The last event in the initiation of protein synthesis in-
other aminoacyl-tRNA in the A site (Fig. 7b) by pep-
volves the joining of the large ribosomal subunit to the
tidyl transferase to form dipeptidyl-tRNA (see Fig. 7c).
pre-initiation complex (Fig. 8). In the prokaryotic sys-
Functional insertion of Met-tRNA f directly into the P site
tem, association of the 50S subunit with the 30S pre-
can be demonstrated using the trinucleotide AUG as a
initiation complex takes place with hydrolysis of GTP by
synthetic mRNA and another trinucleotide, for example
the GTPase activity of IF-2 and release of IF-1, IF-2, GDP,
UUU, to bind an acceptor aminoacyl-tRNA (in this case
and P i . GTP hydrolysis is essential for the release of IF-2
Phe-tRNA).
from the initiation complex, which is a prerequisite for al-
It is possible to measure the peptidyl transferase activity
lowing the fMet-tRNA f to engage in the formation of the
of the large subunit in the absence of mRNA by using
first peptide bond. In eukaryotic protein synthesis, the 80S
the antibiotic puromycin, which resembles the 3 -terminal
initiation complex is formed by joining the 60S ribosomal
region of Phe-tRNA in structure, as an artificial acceptor
subunit to the 48S pre-initiation complex consisting of the
40S ribosomal subunit, eIF-2, eIF-3, GTP, Met-tRNA f , to form methionyl puromycin from Met-tRNA f .
mRNA, and possibly eIF-4C. This coupling reaction re-
quires an additional factor, eIF-5, which mediates the hy- 3. Polypeptide Chain Synthesis: The Elongation–
drolysis of GTP to GDP with release of eIF-2-GDP, P i , Translocation Cycle
and eIF-3 from the 48S pre-initiation complex.
By this stage, all initiation factors have been released This cycle is outlined in Figs. 7b–f.
and are available for recycling, although the exact steps at
which factors are released from intermediate complexes a. Elongation. Thefirstpeptidebondisformedwhen
are not known in every case. There is thus an initiation the aminoacyl-tRNA in the ribosomal A site is converted
factor cycle within the ribosome cycle, and regulation of into the corresponding methionyl-aminoacyl-tRNA by
the activity of factors, particularly eIF-2, is an important transfer of the methionyl (or N-formylmethionyl) residue
control mechanism in translation (see Section V.D.1). from the charged initiator tRNA in the P site (Fig. 7c). In