Page 99 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 99
P1: GTQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017F-788 August 3, 2001 16:27
40 Translation of RNA to Protein
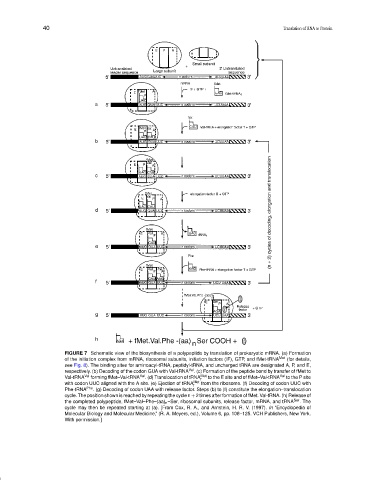
FIGURE 7 Schematic view of the biosynthesis of a polypeptide by translation of prokaryotic mRNA. (a) Formation
of the initiation complex from mRNA, ribosomal subunits, initiation factors (IF), GTP, and fMet-tRNA Met (for details,
see Fig. 8). The binding sites for aminoacyl-tRNA, peptidyl-tRNA, and uncharged tRNA are designated A, P, and E,
respectively. (b) Decoding of the codon GUA with Val-tRNA Val . (c) Formation of the peptide bond by transfer of fMet to
Val-tRNA Val forming fMet–Val-tRNA Val . (d) Translocation of tRNA Met to the E site and of fMet–Val-tRNA Val to the P site
f
with codon UUC aligned with the A site. (e) Ejection of tRNA Met from the ribosome. (f) Decoding of codon UUC with
f
Phe-tRNA Phe . (g) Decoding of codon UAA with release factor. Steps (b) to (f) constitute the elongation–translocation
cycle. The position shown is reached by repeating the cycle n + 2 times after formation of fMet. Val-tRNA. (h) Release of
the completed polypeptide, fMet–Val–Phe–(aa) n –Ser, ribosomal subunits, release factor, mRNA, and tRNA Ser . The
cycle may then be repeated starting at (a). [From Cox, R. A., and Arnstein, H. R. V. (1997). In “Encyclopedia of
Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine,” (R. A. Meyers, ed.), Volume 6, pp. 108–125. VCH Publishers, New York.
With permission.]