Page 229 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 229
Chapter 5. Surface treatments qf,Fhers and effects on composite properties 21 1
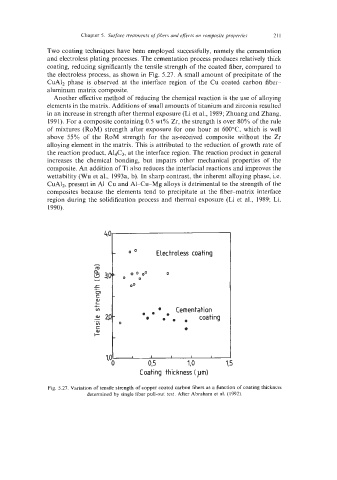
Two coating techniques have been employed successfully, namely the cementation
and electroless plating processes. The cementation process produces relatively thick
coating, reducing significantly the tensile strength of the coated fiber, compared to
the electroless process, as shown in Fig. 5.27. A small amount of precipitate of the
CuA12 phase is observed at the interface region of the Cu coated carbon fiber--
aluminum matrix composite.
Another effective method of reducing the chemical reaction is the use of alloying
elcmcnts in the matrix. Additions of small amounts of titanium and zirconia resulted
in an increase in strength after thermal exposure (Li et al., 1989; Zhuang and Zhang,
1991). For a composite containing 0.5 wt% Zr, the strength is over 80% of the rule
of mixtures (RoM) strength after exposure for one hour at 600°C, which is well
above 55% of the RoM strength for the as-received composite without the Zr
alloying element in the matrix. This is attributed to the reduction of growth rate of
the reaction product, A&, at the interface region. The reaction product in general
increases the chemical bonding, but impairs other mechanical properties of the
composite. An addition of Ti also reduces the interfacial reactions and improves the
wettability (Wu et al., 1993a, b). In sharp contrast, the inherent alloying phase, i.e.
CuA12, present in Al-Cu and Al-Cu-Mg alloys is detrimental to the strength of the
composites because the elements tend to precipitate at the fiber-matrix interface
region during the solidification process and thermal exposure (Li et al., 1989; Li,
1990).
40
- 00 EL ec t roles coating
I
m
El 3P 0 0 00 0
v 0 0
f 00
c -
0-l
a!
L
t
In Cementation
2 a- 0 . 0.. coating
a
.-
In
c
a!
I- -
1 I 1 I I
Fig. 5.27. Variation of tensile strength of copper coated carbon fibers as a function of coating thickness
determined by single fiber pull-out test. After Abraham et al. (1992).