Page 231 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 231
Chapter 5. Surface treatments qfjhers and effects on composite properties 213
Similar to aluminum matrix composites, a major problem encountered with
carbon fiber-Mg matrix composites is the lack of wetting. Deposition of a thin
protective TiB coating on carbon fibers by a CVD process improves the wettability
of magnesium (Katzmann, 1987). However, the TiB coating oxidizes rapidly when
exposed to air, which limits the applications of the coated fibers. Alternatively, a
SOz coating which is stable in air has been applied successfully to improve wetting
(Katzmann, 1987; Chen and Li, 1993). Reaction products, such as Mg2Si and MgO,
are normally precipitated at the interface region of the uncoated fiber. In contrast,
when there is a SOz coating present at the interface, the magnesium matrix reacts
with the coating to form a microprecipitate MgO layer. This reaction is found to
facilitate the infiltration process. Surface treatment of carbon fibers also results in a
marked increase in the interfacial shear strength causing a corresponding decrease in
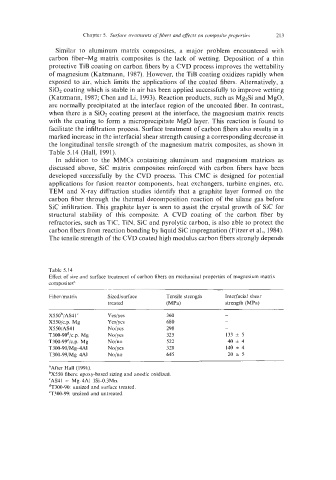
the longitudinal tensile strength of the magnesium matrix composites, as shown in
Table 5.14 (Hall, 1991).
In addition to the MMCs containing aluminum and magnesium matrices as
discussed above, Sic matrix composites reinforced with carbon fibers have been
developed successfully by the CVD process. This CMC is designed for potential
applications for fusion reactor components, heat exchangers, turbine engines, etc.
TEM and X-ray diffraction studies identify that a graphite layer formed on the
carbon fiber through the thermal decomposition reaction of the silane gas before
Sic infiltration. This graphite layer is seen to assist the crystal growth of Sic for
structural stability of this composite. A CVD coating of the carbon fiber by
refractories, such as TIC, TIN, Sic and pyrolytic carbon, is also able to protect the
carbon fibers from reaction bonding by liquid Sic impregnation (Fitzer et al., 1984).
The tensile strength of the CVD coated high modulus carbon fibers strongly depends
Table 5.14
Effect of sine and surface treatment of carbon fibers on mechanical properties of magnesium matrix
composites"
Fiberimatrix Sized/surface Tensile strength Interfacial shear
trcatcd (MW strength (MPa)
X55Ob/AS4Ic Ycs/yes 360 -
X55Oic.p. Mg Ycs/yes 680 -
X550/AS41 No/yes 298 -
T300-90d/c.p. Mg No/ycs 325 133 f 5
T300-99e/c.p. Mg No/no 522 40 f 4
T300-90/Mg4AI Noiycs 328 140 f 4
T300-99/MgAAI No/no 645 20 f 5
aAftcr Hall (1991).
'X550 fibers: epoxy-based sizing and anodic oxidized.
'AS41 = Mg4AI-ISi-0.3Mn.
dT300-90: unsized and surface treated.
'T300-99: unsized and untreated.