Page 245 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 245
226 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
Another good example of interfacial modification can be found in alumina fiber-
glass matrix composites that are essentially an oxide-oxide system. A series of
intermediate compounds has been identified by Aksay and Pask (1975). The reaction
product gives rise to a strong chemical bonding at the interface region and thus a
brittle fracture behavior of the composite (Michasle and Hellman, 1988; Maheshw-
ari et al., 1989). Tin dioxide, Sn02, is known to have no mutual solubility with
aluminum up to 1600°C (Barczak and Insley, 1962), and has a low solubility in silica
(Manfred0 and McNally, 1984). This knowledge has been applied by Chawla et al.,
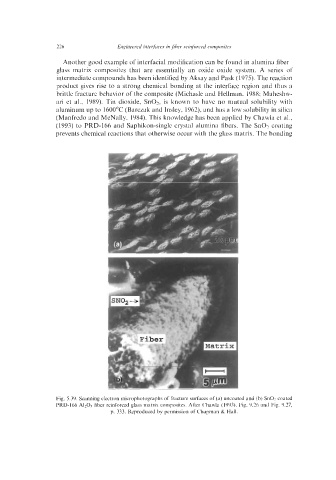
(1993) to PRD-166 and Saphikon-single crystal alumina fibers. The Sn02 coating
prevents chemical reactions that otherwise occur with the glass matrix. The bonding
Fig. 5.39. Scanning electron microphotographs of fracture surfaces of (a) uncoated and (b) Sn02 coated
PRD-166 A1203 fiber reinforced glass matrix composites. After Chawla (1993). Fig. 9.26 and Fig. 9.27,
p. 333. Reproduced by permission of Chapman & Hall.