Page 303 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 303
284 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
giving rise to long fiber pull-out lengths, whereas this mechanism was apparently
absent with the SVF coating.
The effectiveness of the intermittent bonding concept has been confirmed under
adverse environmental conditions, such as hygrothermal aging (Atkins and Mai,
1976). In follow-up studies with Kevlar fiber-epoxy matrix systems (Mai, 1983,
1988; Mai and Castino, 1984, 1985), the coatings based on SVF and a blend of
polyester-polyether resins (Estapol) were explored. The effects of hygrothermal
aging, percentage coating over a repeated fiber length, fatigue damage, strain rate
and temperature on tensile strength, modulus, impact fracture toughness and pull-
out toughness of the composite were investigated. The fracture toughness of
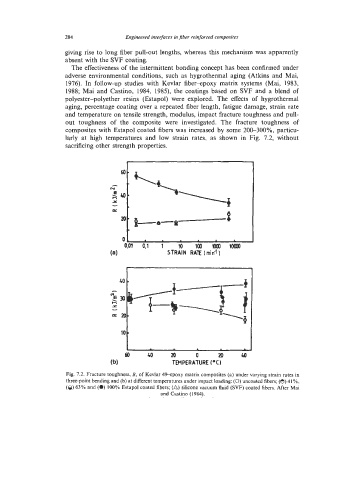
composites with Estapol coated fibers was increased by some 20&300%, particu-
larly at high temperatures and low strain rates, as shown in Fig. 7.2, without
sacrificing other strength properties.
01
0.01 0,l 1 lo 100 XKX) loo00
(a) STRAIN RAlE (mid }
60 20 0 20
(b) TEMPERATURE ('0
Fig. 7.2. Fracture toughness, R, of Kevlar 49-epoxy matrix composites (a) under varying strain rates in
three-point bending and (b) at different temperatures under impact loading: (0) uncoated fibers; (0) 41 %,
(0) 63% and (0) 100% Estapol coated fibers; (A) silicone vacuum fluid (SVF) coated fibers. After Mai
and Castino (1984).