Page 55 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 55
38 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
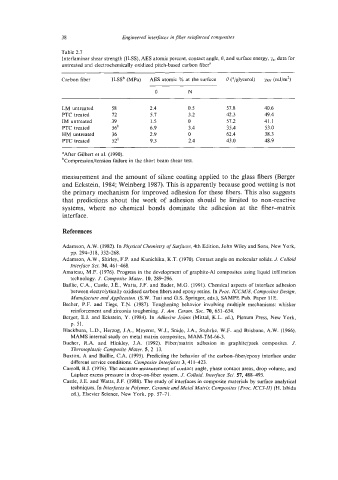
Table 2.7
Interlaminar shear strength (ILSS), AES atomic percent, contact angle, 0, and surface energy, ys. data for
untreated and electrochemically oxidized pitch-based carbon fiber"
Carbon fiber ILSSb (MPa) AES atomic YO at the surface 0 ("/glycerol) ysv (mJ/m2)
0 N
LM untreated 58 2.4 0.5 57.8 40.6
PTC treated 72 5.1 3.2 42.3 49.4
IM untreated 39 1.5 0 57.2 41.1
PTC treated 56' 6.9 3.4 35.4 53.0
HM untreated 36 2.9 0 62.4 38.3
PTC treated 52' 9.3 2.4 43.0 48.9
"After Gilbert et al. (1990).
bCompression/tension failure in the short beam shear test.
measurement and the amount of silane coating applied to the glass fibers (Berger
and Eckstein, 1984; Weinberg 1987). This is apparently because good wetting is not
the primary mechanism for improved adhesion for these fibers. This also suggests
that predictions about the work of adhesion should be limited to non-reactive
systems, where no chemical bonds dominate the adhesion at the fiber-matrix
interface.
References
Adamson, A.W. (1982). In Physical Chemistry ofSurfaces, 4th Edition, John Wiley and Sons, New York,
pp. 294-3 18, 332-268.
Adamson, A.W., Shirley, F.P. and Kunichika, K.T. (1970). Contact angle on molecular solids. J. Colloid
Interface Sei. 34, 461468.
Amateau, M.F. (1976). Progress in the development of graphite-AI composites using liquid infiltration
technology. J, Composite Mater. 10, 289-296.
Baillie, C.A., Castle, J.E., Watts, J.F. and Bader, M.G. (1991). Chemical aspects of interface adhesion
between electrolytically oxidised carbon fibers and epoxy resins. In Proc. ICCM/S, Composites Design,
Manufacture and Application. (S.W. Tsai and G.S. Springer, eds.), SAMPE Pub. Paper 11E.
Becher, P.F. and Tiegs, T.N. (1987). Toughening behavior involving multiple mechanisms: whisker
reinforcement and zirconia toughening. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 70, 651-654.
Berger, E.J. and Eckstein, Y. (1984). In Adhesive Joints (Mittal, K.L. ed.), Plenum Press, New York,
p. 51.
Blackburn, L.D., Herzog, J.A., Meyerer, W.J., Snide, J.A., Stuhrke, W.F. and Brisbane, A.W. (1966).
MAMS internal study on metal matrix composites, MAM-TM-66-3.
Bucher, R.A. and Hinkley, J.A. (1992). Fiber/matrix adhesion in graphite/peek composites. J.
Thermoplastic Composite Mater. 5, 2-13.
Buxton, A and Baillie, C.A. (1995). Predicting the behavior of the carbon-fiber/epoxy interface under
different service conditions. Composite Interfaces 3, 41 1423.
Carroll, B.J. (1976). Thc accurate measurement of contact angle, phase contact areas, drop volume, and
Laplace excess pressure in drop-on-fiber system. J. Colloid. Interface Sei. 57, 488495.
Castle, J.E. and Watts, J.F. (1988). The study of interfaces in composite materials by surface analytical
techniques. In Interfaces in Polymer, Ceramic and Metal Matrix Composites (Proc. ICCI-11) (H. Ishida
ed.), Elsevier Science, New York, pp. 57-71.