Page 50 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 50
Chapter 2. Characterization of interfaces 33
ZI
t
c
v)
al
c
c
c(
I 1 1 I I I
10 15 20 25 30 35
(a) 20 (degrees)
I I I I 1
15 20 25 30 35
(b) 28 (degrees)
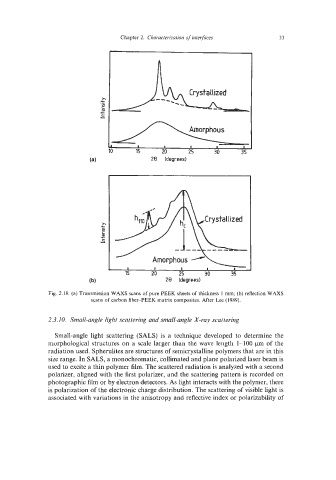
Fig. 2.18. (a) Transmission WAXS scans of pure PEEK sheets of thickness 1 mrn; (b) reflection WAXS
scans of carbon fiber-PEEK matrix composites. After Lee (1989).
2.3.10. Small-angle light scattering and small-angle X-ray scattering
Small-angle light scattering (SALS) is a technique developed to determine the
morphological structures on a scale larger than the wave length 1-100 pm of the
radiation used. Spherulites are structures of semicrystalline polymers that are in this
size range. In SALS, a monochromatic, collimated and plane polarized laser beam is
used to excite a thin polymer film. The scattered radiation is analyzed with a second
polarizer, aligned with the first polarizer, and the scattering pattern is recorded on
photographic film or by electron detectors. As light interacts with the polymer, there
is polarization of the electronic charge distribution. The scattering of visible light is
associated with variations in the anisotropy and reflective index or polarizability of