Page 46 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 46
Chapter 2. Characterization of interfaces 29
I I
I
Unsirei
fiber
Sized
fiber
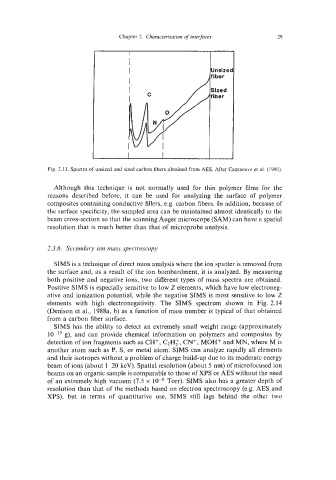
Fig. 2.13. Spectra of unsized and sized carbon fibers obtained from AES. After Cazeneuve et al. (1990).
Although this technique is not normally used for thin polymer films for the
reasons described before, it can be used for analyzing the surface of polymer
composites containing conductive fillers, e.g. carbon fibers. In addition, because of
the surface specificity, the sampled area can be maintained almost identically to the
beam cross-section so that the scanning Auger microscope (SAM) can have a spatial
resolution that is much better than that of microprobe analysis.
2.3.6. Secondary ion mass spectroscopy
SIMS is a technique of direct mass analysis where the ion sputter is removed from
the surface and, as a result of the ion bombardment, it is analyzed. By measuring
both positive and negative ions, two different types of mass spectra are obtained.
Positive SIMS is especially sensitive to low 2 elements, which have low electroneg-
ative and ionization potential, while the negative SIMS is most sensitive to low Z
elements with high electronegativity. The SIMS spectrum shown in Fig. 2.14
(Denison et al., 1988a, b) as a function of mass number is typical of that obtained
from a carbon fiber surface.
SIMS has the ability to detect an extremely small weight range (approximately
lopL5 g), and can provide chemical information on polymers and composites by
detection of ion fragments such as CH+, CzHf, CN+, MOH+ and MN, where M is
another atom such as P, S, or metal atom. SIMS can analyze rapidly all elements
and their isotropes without a problem of charge build-up due to its moderate energy
beam of ions (about 1-20 keV). Spatial resolution (about 5 nm) of microfocused ion
beams on an organic sample is comparable to those of XPS or AES without the need
of an extremely high vacuum (7.5 x Torr). SIMS also has a greater depth of
resolution than that of the methods based on electron spectroscopy (e.g. AES and
XPS), but in terms of quantitative use, SIMS still lags behind the other two