Page 78 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 78
Chapter 3. Measurements of interfacelinterlaminar properties 61
3.3. Interlaminar/intralaminar properties
3.3.1. Introduction
In addition to the direct measurements of fiber-matrix interface properties
discussed in Section 3.2, a number of testing techniques have been devised to assess
the fiber-matrix interface bond quality by inference from the gross mechanical
properties such as interlaminar shear strength (ILSS), translaminar or in-plane shear
strength, and transverse tensile strength. These testing techniques invariably employ
-
m
a -
6
F 100
f -
m 80
c
E 0
0
c -
0
m 0 0
60 0 0
0
- 0 0 0 0
0
40
40 0
1 -
- 0 A A A A o o
0
20
20 - A 1,
A
A A
I
. .
I
1 1
11
0
10
0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 I 5 5 6 6 I 7 6 6 . . 9 9 10 11 fi
7
Laboratory
120
m
CL
z loo(-
F
i 80 - 0
+
m
c
aJ A
L
4- 60 - A 0
m
L 0 0
m A
aJ
r 40 - a A A
m
aJ
U
aJ 20 -
m A
Y- L
4-
c
!--I
(b) Laboratory
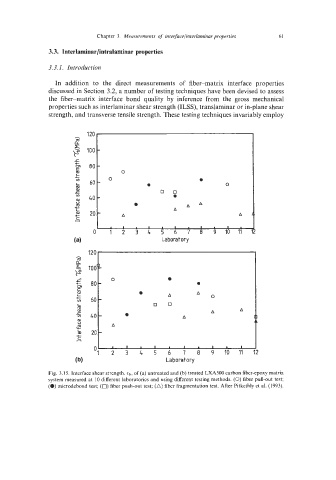
Fig. 3.15. Interface shear strength, Tb, of (a) untreated and (b) treated LXA5OO carbon fiber-epoxy matrix
system measured at 10 different laboratories and using different testing methods. (0) fiber pull-out test;
(a) microdebond test; (0) fiber push-out test; (A) fiber fragmentation test. After Pitkethly et al. (1993).