Page 189 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 189
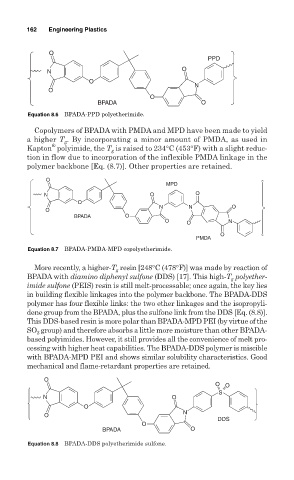
162 Engineering Plastics
O
PPD
O
N
O
N
O
O
BPADA O
Equation 8.6 BPADA-PPD polyetherimide.
Copolymers of BPADA with PMDA and MPD have been made to yield
a higher T . By incorporating a minor amount of PMDA, as used in
g
®
Kapton polyimide, the T is raised to 234°C (453°F) with a slight reduc-
g
tion in flow due to incorporation of the inflexible PMDA linkage in the
polymer backbone [Eq. (8.7)]. Other properties are retained.
O
MPD
N O O
O
N N O
O
BPADA O
O O N
O
PMDA
Equation 8.7 BPADA-PMDA-MPD copolyetherimide.
More recently, a higher-T resin [248°C (478°F)] was made by reaction of
g
BPADA with diamino diphenyl sulfone (DDS) [17]. This high-T polyether-
g
imide sulfone (PEIS) resin is still melt-processable; once again, the key lies
in building flexible linkages into the polymer backbone. The BPADA-DDS
polymer has four flexible links: the two ether linkages and the isopropyli-
dene group from the BPADA, plus the sulfone link from the DDS [Eq. (8.8)].
This DDS-based resin is more polar than BPADA-MPD PEI (by virtue of the
group) and therefore absorbs a little more moisture than other BPADA-
SO 2
based polyimides. However, it still provides all the convenience of melt pro-
cessing with higher heat capabilities. The BPADA-DDS polymer is miscible
with BPADA-MPD PEI and shows similar solubility characteristics. Good
mechanical and flame-retardant properties are retained.
O
O O
S
N O
O
N
O
DDS
O
BPADA O
Equation 8.8 BPADA-DDS polyetherimide sulfone.