Page 67 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 67
Properties 41
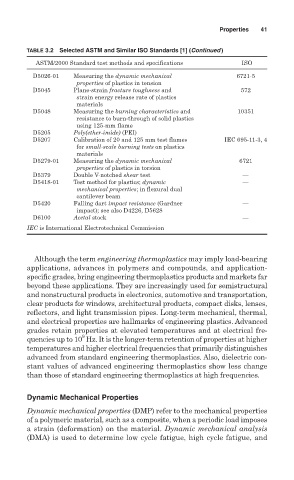
TABLE 3.2 Selected ASTM and Similar ISO Standards [1] (Continued)
ASTM/2000 Standard test methods and specifications ISO
D5026-01 Measuring the dynamic mechanical 6721-5
properties of plastics in tension
D5045 Plane-strain fracture toughness and 572
strain energy release rate of plastics
materials
D5048 Measuring the burning characteristics and 10351
resistance to burn-through of solid plastics
using 125-mm flame
D5205 Poly(ether-imide) (PEI)
D5207 Calibration of 20 and 125 mm test flames IEC 695-11-3, 4
for small-scale burning tests on plastics
materials
D5279-01 Measuring the dynamic mechanical 6721
properties of plastics in torsion
D5379 Double V-notched shear test —
D5418-01 Test method for plastics; dynamic —
mechanical properties; in flexural dual
cantilever beam
D5420 Falling dart impact resistance (Gardner —
impact); see also D4226, D5628
D6100 Acetal stock —
IEC is International Electrotechnical Commission
Although the term engineering thermoplastics may imply load-bearing
applications, advances in polymers and compounds, and application-
specific grades, bring engineering thermoplastics products and markets far
beyond these applications. They are increasingly used for semistructural
and nonstructural products in electronics, automotive and transportation,
clear products for windows, architectural products, compact disks, lenses,
reflectors, and light transmission pipes. Long-term mechanical, thermal,
and electrical properties are hallmarks of engineering plastics. Advanced
grades retain properties at elevated temperatures and at electrical fre-
9
quencies up to 10 Hz. It is the longer-term retention of properties at higher
temperatures and higher electrical frequencies that primarily distinguishes
advanced from standard engineering thermoplastics. Also, dielectric con-
stant values of advanced engineering thermoplastics show less change
than those of standard engineering thermoplastics at high frequencies.
Dynamic Mechanical Properties
Dynamic mechanical properties (DMP) refer to the mechanical properties
of a polymeric material, such as a composite, when a periodic load imposes
a strain (deformation) on the material. Dynamic mechanical analysis
(DMA) is used to determine low cycle fatigue, high cycle fatigue, and