Page 375 - Enhanced Oil Recovery in Shale and Tight Reservoirs
P. 375
Fracturing fluid flow back 347
Vapor Pressure of Water
24,000
Critical
22,000
Point
20,000
18,000
16,000
Pressure [kPa] 14,000
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000 Normal
Triple Boiling
4,000 Point
Point
2,000
0
300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650
Temperature [K]
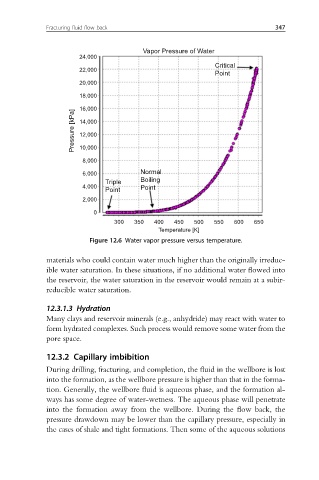
Figure 12.6 Water vapor pressure versus temperature.
materials who could contain water much higher than the originally irreduc-
ible water saturation. In these situations, if no additional water flowed into
the reservoir, the water saturation in the reservoir would remain at a subir-
reducible water saturation.
12.3.1.3 Hydration
Many clays and reservoir minerals (e.g., anhydride) may react with water to
form hydrated complexes. Such process would remove some water from the
pore space.
12.3.2 Capillary imbibition
During drilling, fracturing, and completion, the fluid in the wellbore is lost
into the formation, as the wellbore pressure is higher than that in the forma-
tion. Generally, the wellbore fluid is aqueous phase, and the formation al-
ways has some degree of water-wetness. The aqueous phase will penetrate
into the formation away from the wellbore. During the flow back, the
pressure drawdown may be lower than the capillary pressure, especially in
the cases of shale and tight formations. Then some of the aqueous solutions