Page 107 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 107
100 Entropy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
In Chapter 6, we learned that a reduction in entropy generation corre-
sponds to an increase in thermal efficiency in endoreversible engines. We
now examine the efficiency-entropy production relation in the power
cycles discussed in this chapter at the condition of η com ¼η exp ¼1. For the
ideal Brayton cycle, the thermal efficiency and the normalized entropy gen-
eration read
1 γ
γ (7.49)
η ¼ 1 PR
γ 1
1 γ
1 γ 1
∗ γ PR
Φ ¼ 1 ð + (7.50)
π T R 1Þ T R 1 PR π
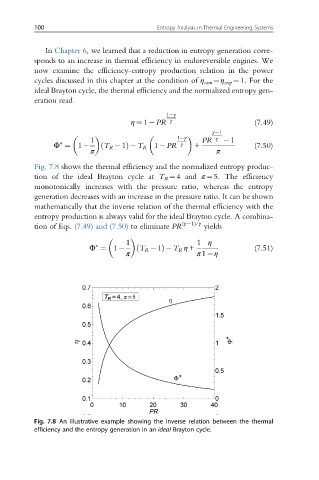
Fig. 7.8 shows the thermal efficiency and the normalized entropy produc-
tion of the ideal Brayton cycle at T R ¼4 and π ¼5. The efficiency
monotonically increases with the pressure ratio, whereas the entropy
generation decreases with an increase in the pressure ratio. It can be shown
mathematically that the inverse relation of the thermal efficiency with the
entropy production is always valid for the ideal Brayton cycle. A combina-
(γ 1)/γ
tion of Eqs. (7.49) and (7.50) to eliminate PR yields
1 1 η
∗
Φ ¼ 1 ð T R 1Þ T R η + (7.51)
π π1 η
Fig. 7.8 An illustrative example showing the inverse relation between the thermal
efficiency and the entropy generation in an ideal Brayton cycle.