Page 130 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 130
Irreversible engines—Open cycles 123
Table 8.4 The operating parameters of the combined cycle.
Parameter Quantity
Gas cycle
298.15K
Ambient temperature, T 0
1bar
Ambient pressure, p 0
1273K
Gas turbine inlet temperature, T 3
0.85
Compressor isentropic efficiency η c
0.90
Gas turbine isentropic efficiency, η t
Steam cycle
30bar
Steam turbine inlet pressure, p 10
0.07bar
Condenser pressure, p 6
400K
Exhaust temperature of flue gases, T 5
0.90
Steam turbine isentropic efficiency, η st
0.70
Condensate pump isentropic efficiency, η cp
0.70
Feed pump isentropic efficiency, η fp
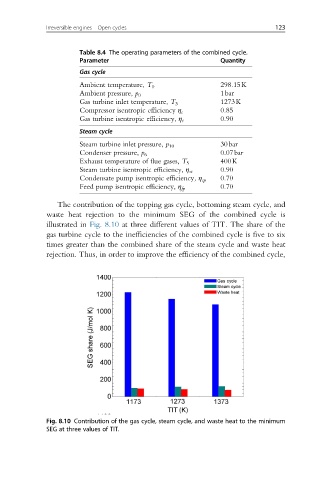
The contribution of the topping gas cycle, bottoming steam cycle, and
waste heat rejection to the minimum SEG of the combined cycle is
illustrated in Fig. 8.10 at three different values of TIT. The share of the
gas turbine cycle to the inefficiencies of the combined cycle is five to six
times greater than the combined share of the steam cycle and waste heat
rejection. Thus, in order to improve the efficiency of the combined cycle,
Fig. 8.10 Contribution of the gas cycle, steam cycle, and waste heat to the minimum
SEG at three values of TIT.