Page 136 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 136
Irreversible engines—Open cycles 129
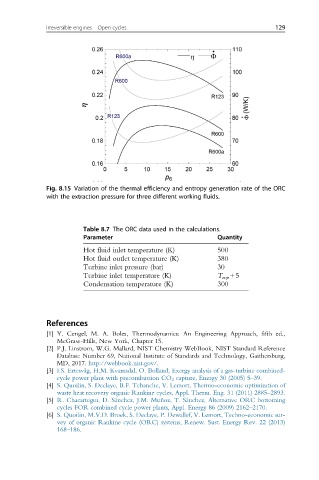
Fig. 8.15 Variation of the thermal efficiency and entropy generation rate of the ORC
with the extraction pressure for three different working fluids.
Table 8.7 The ORC data used in the calculations.
Parameter Quantity
Hot fluid inlet temperature (K) 500
Hot fluid outlet temperature (K) 380
Turbine inlet pressure (bar) 30
Turbine inlet temperature (K) T evp +5
Condensation temperature (K) 300
References
[1] Y. Cengel, M. A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, fifth ed.,
McGraw-Hills, New York, Chapter 15.
[2] P.J. Linstrom, W.G. Mallard, NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference
Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg,
MD, 2017. http://webbook.nist.gov/.
[3] I.S. Ertesva ˚g, H.M. Kvamsdal, O. Bolland, Exergy analysis of a gas-turbine combined-
cycle power plant with precombustion CO 2 capture, Energy 30 (2005) 5–39.
[4] S. Quoilin, S. Declaye, B.F. Tchanche, V. Lemort, Thermo-economic optimization of
waste heat recovery organic Rankine cycles, Appl. Therm. Eng. 31 (2011) 2885–2893.
[5] R. Chacartegui, D. Sa ´nchez, J.M. Mun ˜oz, T. Sa ´nchez, Alternative ORC bottoming
cycles FOR combined cycle power plants, Appl. Energy 86 (2009) 2162–2170.
[6] S. Quoilin, M.V.D. Broek, S. Declaye, P. Dewallef, V. Lemort, Techno-economic sur-
vey of organic Rankine cycle (ORC) systems, Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 22 (2013)
168–186.