Page 52 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 52
Teaching entropy 43
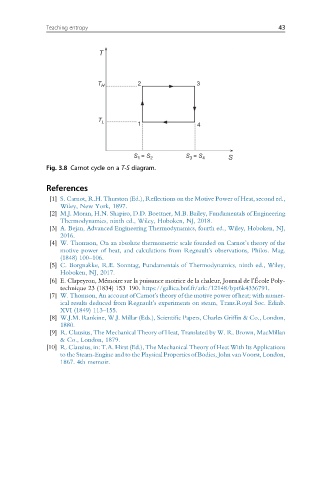
T
T H 2 3
T L 1 4
= S S = S
S 1 2 3 4 S
Fig. 3.8 Carnot cycle on a T-S diagram.
References
[1] S. Carnot, R.H. Thurston (Ed.), Reflections on the Motive Power of Heat, second ed.,
Wiley, New York, 1897.
[2] M.J. Moran, H.N. Shapiro, D.D. Boettner, M.B. Bailey, Fundamentals of Engineering
Thermodynamics, ninth ed., Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2018.
[3] A. Bejan, Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics, fourth ed., Wiley, Hoboken, NJ,
2016.
[4] W. Thomson, On an absolute thermometric scale founded on Carnot’s theory of the
motive power of heat, and calculations from Regnault’s observations, Philos. Mag.
(1848) 100–106.
[5] C. Borgnakke, R.E. Sonntag, Fundamentals of Thermodynamics, ninth ed., Wiley,
Hoboken, NJ, 2017.
[6] E. Clapeyron, M emoire sur la puissance motrice de la chaleur, Journal de l’ Ecole Poly-
technique 23 (1834) 153–190. https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k4336791.
[7] W. Thomson, An account of Carnot’s theory of the motive power of heat; with numer-
ical results deduced from Regnault’s experiments on steam, Trans.Royal Soc. Edinb.
XVI (1849) 113–155.
[8] W.J.M. Rankine, W.J. Millar (Eds.), Scientific Papers, Charles Griffin & Co., London,
1880.
[9] R. Clausius, The Mechanical Theory of Heat, Translated by W. R. Brown, MacMillan
& Co., London, 1879.
[10] R. Clausius, in: T.A. Hirst (Ed.), The Mechanical Theory of Heat With Its Applications
to the Steam-Engine and to the Physical Properties of Bodies, John van Voorst, London,
1867. 4th memoir.