Page 76 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 76
68 Entropy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
Numerous articles have appeared in the literature claiming a direct relation-
ship between the entropy produced by a power-producing system and its
thermal efficiency. In some cases, a relation between the maximum work
production and the minimum entropy generation has been observed [5–8].
The present chapter investigates the equivalence of maximum thermal
efficiency and minimum entropy production in typical endoreversible
engines, including the models of Curzon-Ahlborn [9], Novikov [10], mod-
ified Novikov, and Carnot vapor cycle. It is aimed to show that the thermal
efficiency of a heat engine may correlate with the entropy generation asso-
ciated with the operation of that engine if the engine is endoreversible. The
thermal efficiency and the power output of these engines at the condition of
minimum entropy generation rate will also be examined.
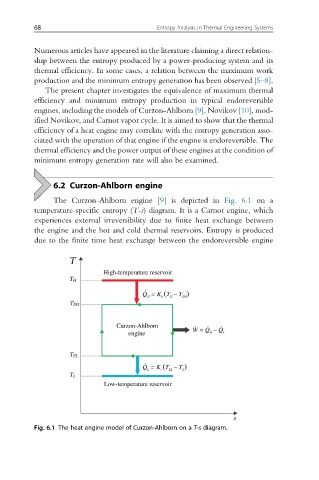
6.2 Curzon-Ahlborn engine
The Curzon-Ahlborn engine [9] is depicted in Fig. 6.1 on a
temperature-specific entropy (T-s) diagram. It is a Carnot engine, which
experiences external irreversibility due to finite heat exchange between
the engine and the hot and cold thermal reservoirs. Entropy is produced
due to the finite time heat exchange between the endoreversible engine
Fig. 6.1 The heat engine model of Curzon-Ahlborn on a T-s diagram.