Page 162 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 162
148 Principles and Methods
3 4
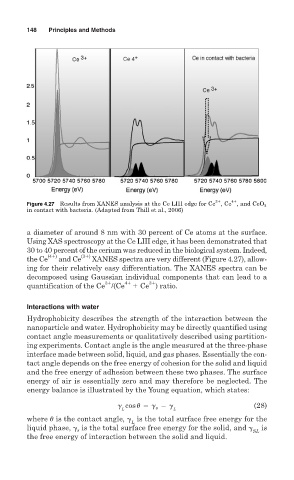
Figure 4.27 Results from XANES analysis at the Ce LIII edge for Ce , Ce , and CeO 2
in contact with bacteria. (Adapted from Thill et al., 2006)
a diameter of around 8 nm with 30 percent of Ce atoms at the surface.
Using XAS spectroscopy at the Ce LIII edge, it has been demonstrated that
30 to 40 percent of the cerium was reduced in the biological system. Indeed,
the Ce (4 ) and Ce (3 ) XANES spectra are very different (Figure 4.27), allow-
ing for their relatively easy differentiation. The XANES spectra can be
decomposed using Gaussian individual components that can lead to a
3 4 3
quantification of the Ce /(Ce Ce ) ratio.
Interactions with water
Hydrophobicity describes the strength of the interaction between the
nanoparticle and water. Hydrophobicity may be directly quantified using
contact angle measurements or qualitatively described using partition-
ing experiments. Contact angle is the angle measured at the three-phase
interface made between solid, liquid, and gas phases. Essentially the con-
tact angle depends on the free energy of cohesion for the solid and liquid
and the free energy of adhesion between these two phases. The surface
energy of air is essentially zero and may therefore be neglected. The
energy balance is illustrated by the Young equation, which states:
g cos u 5 g 2 g (28)
s
L L
where u is the contact angle, is the total surface free energy for the
L
liquid phase, is the total surface free energy for the solid, and SL is
s
the free energy of interaction between the solid and liquid.