Page 250 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 250
Nanoparticle Transport, Aggregation, and Deposition 235
infinitely long flat plates [3]. Using Derjaguin’s approximation the LW
interaction energy between a flat surface and a spherical particle may
be calculated as follows:
Aa 21
LW p 14h
U 123 52a ba1 1 b (2)
6h l
where A is the Hamaker constant for the interacting surfaces across the
medium; is the characteristic wavelength of the dielectric, usually
taken to be equal to 100 nm; a p is the radius of the spherical particle;
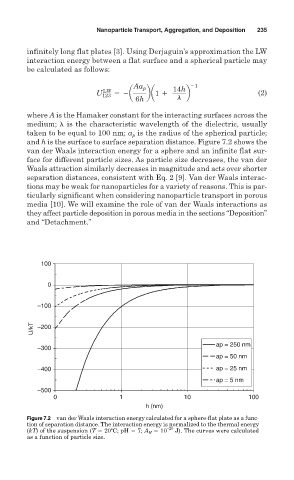
and h is the surface to surface separation distance. Figure 7.2 shows the
van der Waals interaction energy for a sphere and an infinite flat sur-
face for different particle sizes. As particle size decreases, the van der
Waals attraction similarly decreases in magnitude and acts over shorter
separation distances, consistent with Eq. 2 [9]. Van der Waals interac-
tions may be weak for nanoparticles for a variety of reasons. This is par-
ticularly significant when considering nanoparticle transport in porous
media [10]. We will examine the role of van der Waals interactions as
they affect particle deposition in porous media in the sections “Deposition”
and “Detachment.”
100
0
–100
U/kT –200
ap = 250 nm
–300
ap = 50 nm
–400 ap = 25 nm
ap = 5 nm
–500
0 1 10 100
h (nm)
Figure 7.2 van der Waals interaction energy calculated for a sphere-flat plate as a func-
tion of separation distance. The interaction energy is normalized to the thermal energy
(kT) of the suspension (T 20ºC; pH 7; A H 10 –20 J). The curves were calculated
as a function of particle size.