Page 107 - Essentials of physical chemistry
P. 107
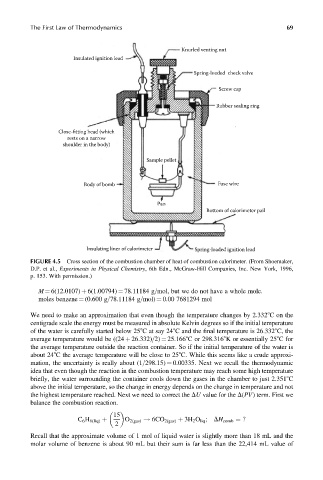
The First Law of Thermodynamics 69
Knurled venting nut
Insulated ignition lead
Spring-loaded check valve
Screw cap
Rubber sealing ring
Close-fitting head (which
rests on a narrow
shoulder in the body)
Sample pellet
Body of bomb Fuse wire
Pan
Bottom of calorimeter pail
Insulating liner of calorimeter Spring-loaded ignition lead
FIGURE 4.5 Cross section of the combustion chamber of heat of combustion calorimeter. (From Shoemaker,
D.P. et al., Experiments in Physical Chemistry, 6th Edn., McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. New York, 1996,
p. 153. With permission.)
M ¼ 6(12.0107) þ 6(1.00794) ¼ 78.11184 g=mol, but we do not have a whole mole.
moles benzene ¼ (0.600 g=78.11184 g=mol) ¼ 0.00 7681294 mol
We need to make an approximation that even though the temperature changes by 2.3328C on the
centigrade scale the energy must be measured in absolute Kelvin degrees so if the initial temperature
of the water is carefully started below 258C at say 248C and the final temperature is 26.3328C, the
average temperature would be ((24 þ 26.332)=2) ¼ 25.1668C or 298.3168K or essentially 258C for
the average temperature outside the reaction container. So if the initial temperature of the water is
about 248C the average temperature will be close to 258C. While this seems like a crude approxi-
mation, the uncertainty is really about (1=298.15) ¼ 0.00335. Next we recall the thermodynamic
idea that even though the reaction in the combustion temperature may reach some high temperature
briefly, the water surrounding the container cools down the gases in the chamber to just 2.3518C
above the initial temperature, so the change in energy depends on the change in temperature and not
the highest temperature reached. Next we need to correct the DU value for the D(PV) term. First we
balance the combustion reaction.
15
O 2(gas) ! 6CO 2(gas) þ 3H 2 O liq ; DH comb ¼ ?
C 6 H 6(liq) þ
2
Recall that the approximate volume of 1 mol of liquid water is slightly more than 18 mL and the
molar volume of benzene is about 90 mL but their sum is far less than the 22,414 mL value of