Page 120 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 120
PIPING
2.70 CHAPTER TWO
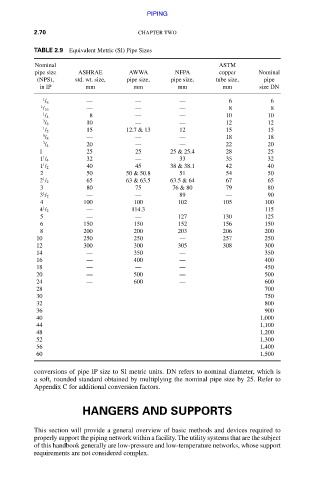
TABLE 2.9 Equivalent Metric (SI) Pipe Sizes
Nominal ASTM
pipe size ASHRAE AWWA NFPA copper Nominal
(NPS), std. wt. size, pipe size, pipe size, tube size, pipe
in IP mm mm mm mm size DN
1 / 8 — — — 6 6
1 — — — 8 8
/ 16
1 8 — — 10 10
/ 4
3 10 — — 12 12
/ 8
1 / 2 15 12.7 & 13 12 15 15
5 — — — 18 18
/ 8
3 20 — — 22 20
/ 4
1 25 25 25 & 25.4 28 25
1
1 / 4 32 — 33 35 32
1 / 2 40 45 38 & 38.1 42 40
1
2 50 50 & 50.8 51 54 50
2 / 2 65 63 & 63.5 63.5 & 64 67 65
1
3 80 75 76 & 80 79 80
1 — — 89 — 90
3 / 2
4 100 100 102 105 100
1 — 114.3 115
4 / 2
5 — — 127 130 125
6 150 150 152 156 150
8 200 200 203 206 200
10 250 250 — 257 250
12 300 300 305 308 300
14 — 350 — 350
16 — 400 — 400
18 — — — 450
20 — 500 — 500
24 — 600 — 600
28 700
30 750
32 800
36 900
40 1,000
44 1,100
48 1,200
52 1,300
56 1,400
60 1,500
conversions of pipe IP size to SI metric units. DN refers to nominal diameter, which is
a soft, rounded standard obtained by multiplying the nominal pipe size by 25. Refer to
Appendix C for additional conversion factors.
HANGERS AND SUPPORTS
This section will provide a general overview of basic methods and devices required to
properly support the piping network within a facility. The utility systems that are the subject
of this handbook generally are low-pressure and low-temperature networks, whose support
requirements are not considered complex.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.