Page 209 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 209
WATER TREATMENT AND PURIFICATION
WATER TREATMENT AND PURIFICATION 4.45
7. Sterile water for inhalation. WFI sterilized and suitably packaged. It contains no antimi-
crobial agent, except when used in humidifiers or similar devices subject to contamina-
tion, or other added substances.
8. Sterile water for irrigation. WFI sterilized and suitably packaged. It contains no antimi-
crobial agent.
PHARMACEUTICAL WATER TREATMENT
PROCESS
Pharmaceutical water treatment takes raw water that meets drinking (potable) water stan-
dards and removes sufficient contaminants from that water in a treatment plant to meet the
standards for the various types of compendial waters. It takes a number of treatment steps
in order to process raw water into PW and other subsequent pure water types.
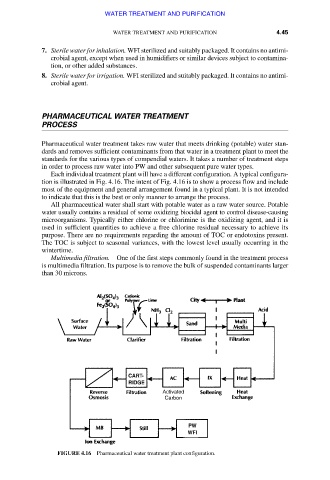
Each individual treatment plant will have a different configuration. A typical configura-
tion is illustrated in Fig. 4.16. The intent of Fig. 4.16 is to show a process flow and include
most of the equipment and general arrangement found in a typical plant. It is not intended
to indicate that this is the best or only manner to arrange the process.
All pharmaceutical water shall start with potable water as a raw water source. Potable
water usually contains a residual of some oxidizing biocidal agent to control disease-causing
microorganisms. Typically either chlorine or chlorimine is the oxidizing agent, and it is
used in sufficient quantities to achieve a free chlorine residual necessary to achieve its
purpose. There are no requirements regarding the amount of TOC or endotoxins present.
The TOC is subject to seasonal variances, with the lowest level usually occurring in the
wintertime.
Multimedia filtration. One of the first steps commonly found in the treatment process
is multimedia filtration. Its purpose is to remove the bulk of suspended contaminants larger
than 30 microns.
FIGURE 4.16 Pharmaceutical water treatment plant configuration.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.