Page 58 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 58
43
* SafetyFactor
0 Maximum Moment (kN*m) - Hac
n
7
6
5 w
R
4 $
0
-l
3 =
5
2r“
1
0
FLAC predicted Deflections, 6, (cm)
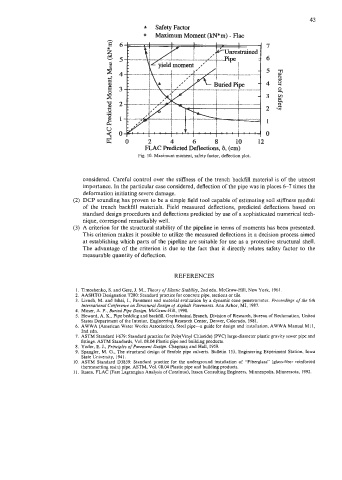
Fig. IO. Maximum moment, safety factor, deflection plot.
considered. Careful control over the stiffness of the trench backfill material is of the utmost
importance. In the particular case considered, deflection of the pipe was in places 6-7 times the
deformation initiating severe damage.
(2) DCP sounding has proven to be a simple field tool capable of estimating soil stiffness moduli
of the trench backfill materials. Field measured deflections, predicted deflections based on
standard design procedures and deflections predicted by use of a sophisticated numerical tech-
nique, correspond remarkably well.
(3) A criterion for the structural stability of the pipeline in terms of moments has been presented.
This criterion makes it possible to utilize the measured deflections in a decision process aimed
at establishing which parts of the pipeline are suitable for use as a protective structural shell.
The advantage of the criterion is due to the fact that it directly relates safety factor to the
measurable quantity of deflection.
REFERENCES
I. Timoshenko, S. and Gere, J. M., Theory ofEZastic Sfabiliry, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1961.
2. AASHTO Designation T280 Standard practice for concrete pipe, sections or tile.
3. Livneh, M. and Ishai, I., Pavement and material evaluation by a dynamic cone penetrometer. Proceedings offhe 6th
Internarional Conference on Structural Design of’dsphal! Pavements. Ann Arbor, MI, 1987.
4. Moser, A. P., Buried Pipe Design. McGraw-Hill, 1990.
5. Howard, A. K., Pipe bedding and backfill. Geotechnical Branch, Division of Research, Bureau of Reclamation, United
States Department of the Interior, Engineering Research Center, Denver, Colorado, 198 1.
6. AWWA (American Water Works Association), Steel pipe-a guide for design and installation, AWWA Manual M 1 I,
2nd edn.
7. ASTM Standard F679 Standard practice for Poly(Viny1 Chloride) (PVC) large-diameter plastic gravity sewer pipe and
fittings. ASTM Standards, Vol. 08.04 Plastic pipe and building products.
8. Yoder, E. J., Principles ofPauement Design. Chapman and Hall, 1959.
9. Spangler, M. G., The structural design of flexible pipe culverts. Bulletin 153, Engineering Experiment Station, Iowa
State University, 1941.
IO. ASTM Standard D3839: Standard practice for the underground installation of “Fiberglass” (glass-fiber reinforced
thermosetting resin) pipe. ASTM, Vol. 08.04 Plastic pipe and building products.
I 1. Itasca, FLAC (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua), Itasca Consulting Engineers, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 1992.