Page 539 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 539
JWCL344_ch13_457-499.qxd 8/7/10 8:49 PM Page 497
Problems/Questions 497
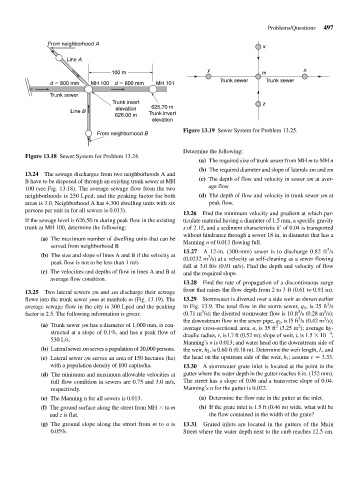
From neighborhood A
x
Line A
y n
100 m m
Trunk sewer Trunk sewer
d 800 mm MH 100 d 800 mm MH 101
Trunk sewer
Trunk invert z
elevation 625.70 m
Line B
626.00 m Trunk invert
elevation
Figure 13.19 Sewer System for Problem 13.25.
From neighborhood B
Determine the following:
Figure 13.18 Sewer System for Problem 13.24.
(a) The required size of trunk sewer from MH m to MH n
(b) The required diameter and slope of laterals xm and zm
13.24 The sewage discharges from two neighborhoods A and
(c) The depth of flow and velocity in sewer xm at aver-
B have to be disposed of through an existing trunk sewer at MH
age flow
100 (see Fig. 13.18). The average sewage flow from the two
neighborhoods is 250 Lpcd, and the peaking factor for both (d) The depth of flow and velocity in trunk sewer ym at
areas is 3.0. Neighborhood A has 4,300 dwelling units with six peak flow.
persons per unit (n for all sewers is 0.013).
13.26 Find the minimum velocity and gradient at which par-
If the sewage level is 626.50 m during peak flow in the existing ticulate material having a diameter of 1.5 mm, a specific gravity
trunk at MH 100, determine the following: s of 2.15, and a sediment characteristic k of 0.04 is transported
without hindrance through a sewer 18 in. in diameter that has a
(a) The maximum number of dwelling units that can be
Manning n of 0.013 flowing full.
served from neighborhood B
3
13.27 A 12-in. (300-mm) sewer is to discharge 0.82 ft /s
(b) The size and slope of lines A and B if the velocity at 3
(0.0232 m /s) at a velocity as self-cleaning as a sewer flowing
peak flow is not to be less than 1 m/s
full at 3.0 ft/s (0.91 m/s). Find the depth and velocity of flow
(c) The velocities and depths of flow in lines A and B at and the required slope.
average flow condition.
13.28 Find the rate of propagation of a discontinuous surge
front that raises the flow depth from 2 to 3 ft (0.61 to 0.91 m).
13.25 Two lateral sewers zm and xm discharge their sewage
flows into the trunk sewer ymn at manhole m (Fig. 13.19). The 13.29 Stormwater is diverted over a side weir as shown earlier
3
average sewage flow in the city is 300 Lpcd and the peaking in Fig. 13.9. The total flow in the storm sewer, q 1 , is 25 ft /s
3
3
3
factor is 2.5. The following information is given: (0.71 m /s); the diverted stormwater flow is 10 ft /s (0.28 m /s);
3
3
the downstream flow in the sewer pipe, q 2 , is l5 ft /s (0.42 m /s);
(a) Trunk sewer ym has a diameter of 1,000 mm, is con- 2 2
average cross-sectional area, a, is 35 ft (3.25 m ); average hy-
structed at a slope of 0.1%, and has a peak flow of 4
draulic radius, r, is l.7 ft (0.52 m); slope of weir, i, is 1.5 10 ;
530 L/s.
Manning’s n is 0.013; and water head on the downstream side of
(b) Lateral sewer xm serves a population of 20,000 persons. the weir, h 2 , is 0.60 ft (0.18 m). Determine the weir length, L, and
(c) Lateral sewer zm serves an area of 150 hectares (ha) the head on the upstream side of the weir, h 1 ; assume c 3.33.
with a population density of 100 capita/ha. 13.30 A stormwater grate inlet is located at the point in the
(d) The minimum and maximum allowable velocities at gutter where the water depth in the gutter reaches 6 in. (152 mm).
full flow condition in sewers are 0.75 and 3.0 m/s, The street has a slope of 0.06 and a transverse slope of 0.04.
respectively. Manning’s n for the gutter is 0.022.
(e) The Manning n for all sewers is 0.013. (a) Determine the flow rate in the gutter at the inlet.
(f) The ground surface along the street from MH to m (b) If the grate inlet is 1.5 ft (0.46 m) wide, what will be
and z is flat. the flow contained in the width of the grate?
(g) The ground slope along the street from m to n is 13.31 Grated inlets are located in the gutters of the Main
0.05%. Street where the water depth next to the curb reaches 12.5 cm.