Page 79 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 79
58 Chapters Fabrication of Bragg Gratings
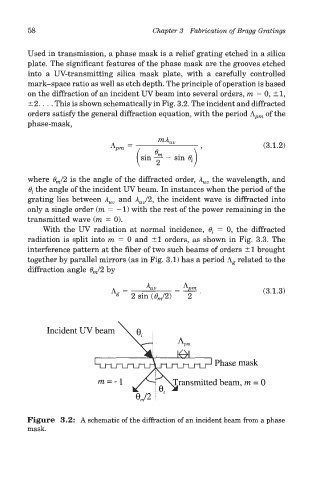
Used in transmission, a phase mask is a relief grating etched in a silica
plate. The significant features of the phase mask are the grooves etched
into a UV-transmitting silica mask plate, with a carefully controlled
mark-space ratio as well as etch depth. The principle of operation is based
on the diffraction of an incident UV beam into several orders, m = 0, ±1,
±2. ... This is shown schematically in Fig. 3.2. The incident and diffracted
orders satisfy the general diffraction equation, with the period A pm of the
phase-mask,
where 0 m/2 is the angle of the diffracted order, A uv the wavelength, and
0j the angle of the incident UV beam. In instances when the period of the
grating lies between A uv and A Ml/2, the incident wave is diffracted into
only a single order (m = -1) with the rest of the power remaining in the
transmitted wave (m = 0).
With the UV radiation at normal incidence, ^ = 0, the diffracted
radiation is split into m = 0 and ±1 orders, as shown in Fig. 3.3. The
interference pattern at the fiber of two such beams of orders ± 1 brought
together by parallel mirrors (as in Fig. 3.1) has a period A^ related to the
diffraction angle # m/2 by
Figure 3.2: A schematic of the diffraction of an incident beam from a phase
mask.