Page 84 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 84
3.1 Methods for fiber Bragg grating fabrication 63
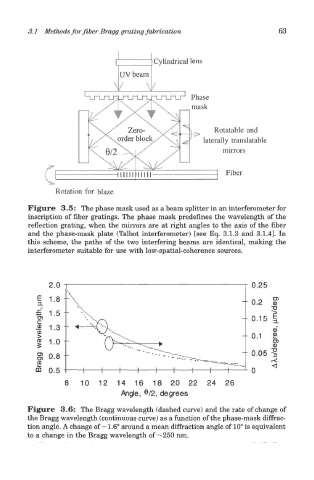
Figure 3.5: The phase mask used as a beam splitter in an interferometer for
inscription of fiber gratings. The phase mask predefines the wavelength of the
reflection grating, when the mirrors are at right angles to the axis of the fiber
and the phase-mask plate (Talbot interferometer) [see Eq. 3.1.3 and 3.1.4]. In
this scheme, the paths of the two interfering beams are identical, making the
interferometer suitable for use with low-spatial-coherence sources.
Figure 3.6: The Bragg wavelength (dashed curve) and the rate of change of
the Bragg wavelength (continuous curve) as a function of the phase-mask diffrac-
tion angle. A change of —1.6° around a mean diffraction angle of 10° is equivalent
to a change in the Bragg wavelength of —250 nm.