Page 63 - Fiber Fracture
P. 63
48 M. Elices and J. Llorca
TRANSVERSAL LONGITUDINAL
SECTION SECTION
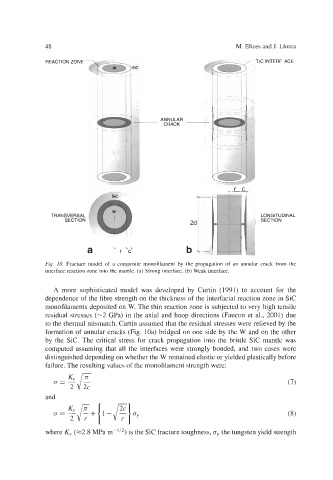
Fig. 10. Fracture model of a composite monofilament by the propagation of an annular crack from the
interface reaction zone into the mantle. (a) Strong interface. (b) Weak interface.
A more sophisticated model was developed by Curtin (1991) to account for the
dependence of the fibre strength on the thickness of the interfacial reaction zone in Sic
monofilaments deposited on W. The thin reaction zone is subjected to very high tensile
residual stresses (-2 GPa) in the axial and hoop directions (Faucon et al., 2001) due
to the thermal mismatch. Curtin assumed that the residual stresses were relieved by the
formation of annular cracks (Fig. loa) bridged on one side by the W and on the other
by the Sic. The critical stress for crack propagation into the brittle Sic mantle was
computed assuming that all the interfaces were strongly bonded, and two cases were
distinguished depending on whether the W remained elastic or yielded plastically before
failure. The resulting values of the monofilament strength were:
g = “J- n
(7)
2 2c
and
where K, (~2.8 MPa m-l”) is the Sic fracture toughness, ay the tungsten yield strength