Page 145 - Finite Element Analysis with ANSYS Workbench
P. 145
136 Chapter 8 Failure Analysis
The distortion energy theory is another popular theory.
With the von-Mises criterion, the theory states that,
max yield
where max is the maximum von-Mises stress.
It is noted that the maximum stresses above are reduced
by the safety factor n for problems in application.
8.1 Buckling
8.1.1 Fundamentals
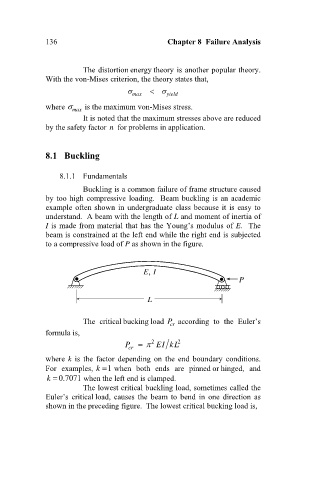
Buckling is a common failure of frame structure caused
by too high compressive loading. Beam buckling is an academic
example often shown in undergraduate class because it is easy to
understand. A beam with the length of L and moment of inertia of
I is made from material that has the Young’s modulus of E. The
beam is constrained at the left end while the right end is subjected
to a compressive load of P as shown in the figure.
E, I
P
L
The critical bucking load P according to the Euler’s
cr
formula is,
2
P 2 EI kL
cr
where k is the factor depending on the end boundary conditions.
For examples, k 1 when both ends are pinned or hinged, and
k 0.7071 when the left end is clamped.
The lowest critical buckling load, sometimes called the
Euler’s critical load, causes the beam to bend in one direction as
shown in the preceding figure. The lowest critical bucking load is,