Page 230 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 230
Plate and Shell Analyses 215
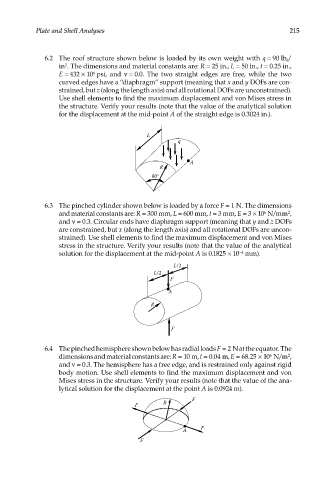
6.2 The roof structure shown below is loaded by its own weight with q = 90 lb /
f
in . The dimensions and material constants are: R = 25 in., L = 50 in., t = 0.25 in.,
2
E = 432 × 10 psi, and ν = 0.0. The two straight edges are free, while the two
6
curved edges have a “diaphragm” support (meaning that x and y DOFs are con-
strained, but z (along the length axis) and all rotational DOFs are unconstrained).
Use shell elements to find the maximum displacement and von Mises stress in
the structure. Verify your results (note that the value of the analytical solution
for the displacement at the mid-point A of the straight edge is 0.3024 in.).
L
q
A
R
80°
6.3 The pinched cylinder shown below is loaded by a force F = 1 N. The dimensions
and material constants are: R = 300 mm, L = 600 mm, t = 3 mm, E = 3 × 10 N/mm ,
2
6
and ν = 0.3. Circular ends have diaphragm support (meaning that y and z DOFs
are constrained, but x (along the length axis) and all rotational DOFs are uncon-
strained). Use shell elements to find the maximum displacement and von Mises
stress in the structure. Verify your results (note that the value of the analytical
solution for the displacement at the mid-point A is 0.1825 × 10 mm).
−4
L/2
L/2
F
A
R
F
6.4 The pinched hemisphere shown below has radial loads F = 2 N at the equator. The
6
dimensions and material constants are: R = 10 m, t = 0.04 m, E = 68.25 × 10 N/m ,
2
and ν = 0.3. The hemisphere has a free edge, and is restrained only against rigid
body motion. Use shell elements to find the maximum displacement and von
Mises stress in the structure. Verify your results (note that the value of the ana-
lytical solution for the displacement at the point A is 0.0924 m).
F
F R
A F
F