Page 345 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 345
336 Chapter 14
Finally,
h h
h 5 r arctan2 sin ; cos : (14.9)
r r
We utilize arctan 2 for h and θ 2 (14.3) to keep respective quadrant information and return
the correct quadrant during calculations.
Therefore the kinematic relation can be described by
2 s ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 3
2
p ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
2
z 2 r 1 2 12 1 x 1y 2
r
6 7
6 7
2 3 6 7
s ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
!
L 1 6 2 7
p ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 1 p
6 1 ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi 7
h 1 2 12 2 2 ; 1 2 2 :
4 5 5 r arctan2 x 1y x 1 y 2 7
6
r
6 r 7
θ 2 6 7
!
6 7
x
6 7
arctan2
4 5
y
14.5 Control system
14.5.1 Motor driver
A QZ-DCC9010 DC servo motor driver (Table 14.2) was selected as the motor controller
for the CTR. The QZ-DCC9010 has an inbuilt proportional integral derivative (PID)
controller capable of working in various modes independent of an external controller
(Fig. 14.8), with an accuracy that surpasses previous efforts with controllers such as the
Arduino. Equipped with an encoder tracking, it is possible to program the controller directly
for control of the motors (Fig. 14.9) and produce graphs from the QZ driver debugger
(Fig. 14.10).
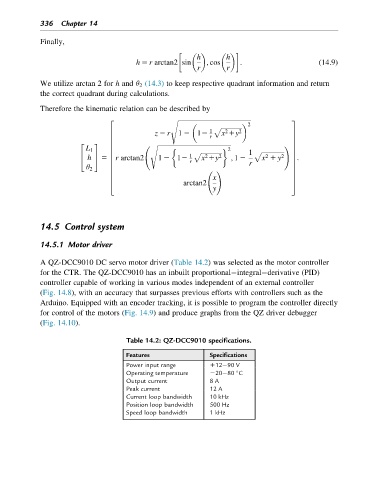
Table 14.2: QZ-DCC9010 specifications.
Features Specifications
Power input range 112 90 V
Operating temperature 220 80 C
Output current 8 A
Peak current 12 A
Current loop bandwidth 10 kHz
Position loop bandwidth 500 Hz
Speed loop bandwidth 1 kHz