Page 430 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 430
424 Chapter 19
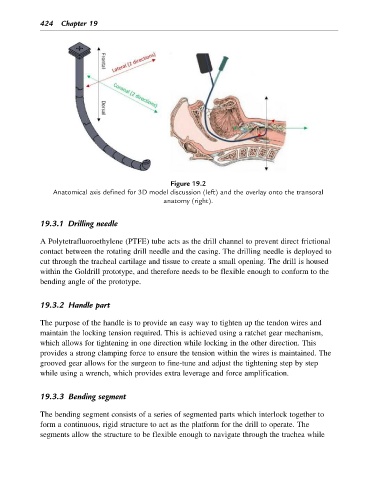
Figure 19.2
Anatomical axis defined for 3D model discussion (left) and the overlay onto the transoral
anatomy (right).
19.3.1 Drilling needle
A Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) tube acts as the drill channel to prevent direct frictional
contact between the rotating drill needle and the casing. The drilling needle is deployed to
cut through the tracheal cartilage and tissue to create a small opening. The drill is housed
within the Goldrill prototype, and therefore needs to be flexible enough to conform to the
bending angle of the prototype.
19.3.2 Handle part
The purpose of the handle is to provide an easy way to tighten up the tendon wires and
maintain the locking tension required. This is achieved using a ratchet gear mechanism,
which allows for tightening in one direction while locking in the other direction. This
provides a strong clamping force to ensure the tension within the wires is maintained. The
grooved gear allows for the surgeon to fine-tune and adjust the tightening step by step
while using a wrench, which provides extra leverage and force amplification.
19.3.3 Bending segment
The bending segment consists of a series of segmented parts which interlock together to
form a continuous, rigid structure to act as the platform for the drill to operate. The
segments allow the structure to be flexible enough to navigate through the trachea while