Page 445 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 445
Flexible drill manipulator utilizing different rolling sliding joints for transoral drilling 439
• Once comfortable with the drilling position, insert a flexible drill bit (2 mm diameter,
steel) from the hole at the back of the handle and attach it to a surgical drill and
perform the drilling operation.
• Once the drilling is done, he can retract the drill bit, disengage the ratchet, and release
trigger to loosen the Goldrill tube before retraction.
19.6 Design verification tests
19.6.1 INSTRON tests
19.6.1.1 The tensile stress of tendon wires
To ensure that the tendon wires do not snap during the operation, tensile testing was
conducted on small, medium, and large wires of similar structure but varying thickness.
The results are summarized below:
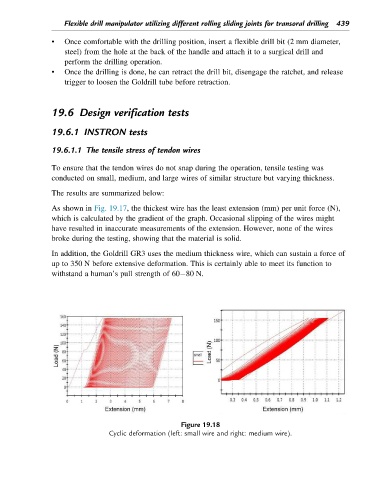
As shown in Fig. 19.17, the thickest wire has the least extension (mm) per unit force (N),
which is calculated by the gradient of the graph. Occasional slipping of the wires might
have resulted in inaccurate measurements of the extension. However, none of the wires
broke during the testing, showing that the material is solid.
In addition, the Goldrill GR3 uses the medium thickness wire, which can sustain a force of
up to 350 N before extensive deformation. This is certainly able to meet its function to
withstand a human’s pull strength of 60 80 N.
Figure 19.18
Cyclic deformation (left: small wire and right: medium wire).