Page 317 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 317
298 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
U
r 1 b
2
a 2
1
W 2 c 2
2
Blade motion
3 b 3
c = c x W 3
3
Exit U
flow
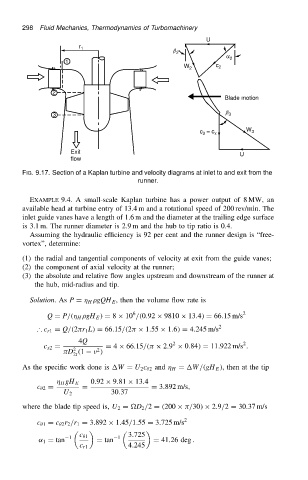
FIG. 9.17. Section of a Kaplan turbine and velocity diagrams at inlet to and exit from the
runner.
EXAMPLE 9.4. A small-scale Kaplan turbine has a power output of 8 MW, an
available head at turbine entry of 13.4 m and a rotational speed of 200 rev/min. The
inlet guide vanes have a length of 1.6 m and the diameter at the trailing edge surface
is 3.1 m. The runner diameter is 2.9 m and the hub to tip ratio is 0.4.
Assuming the hydraulic efficiency is 92 per cent and the runner design is “free-
vortex”, determine:
(1) the radial and tangential components of velocity at exit from the guide vanes;
(2) the component of axial velocity at the runner;
(3) the absolute and relative flow angles upstream and downstream of the runner at
the hub, mid-radius and tip.
Solution.As P D H gQH E , then the volume flow rate is
6
Q D P/. H gH E / D 8 ð 10 /.0.92 ð 9810 ð 13.4/ D 66.15 m/s 2
∴ c r1 D Q/.2 r 1 L/ D 66.15/.2 ð 1.55 ð 1.6/ D 4.245 m/s 2
4Q 2 2
c x2 D 2 D 4 ð 66.15/. ð 2.9 ð 0.84/ D 11.922 m/s .
2
D .1 /
2t
As the specific work done is W D U 2 c 2 and H D W/.gH E /, then at the tip
0.92 ð 9.81 ð 13.4
H gH E
c 2 D D D 3.892 m/s,
U 2 30.37
where the blade tip speed is, U 2 D D 2 /2 D .200 ð /30/ ð 2.9/2 D 30.37 m/s
c 1 D c 2 r 2 /r 1 D 3.892 ð 1.45/1.55 D 3.725 m/s 2
3.725
˛ 1 D tan 1 c 1 D tan 1 D 41.26 deg .
c r1 4.245