Page 488 - Fluid-Structure Interactions Slender Structure and Axial Flow (Volume 1)
P. 488
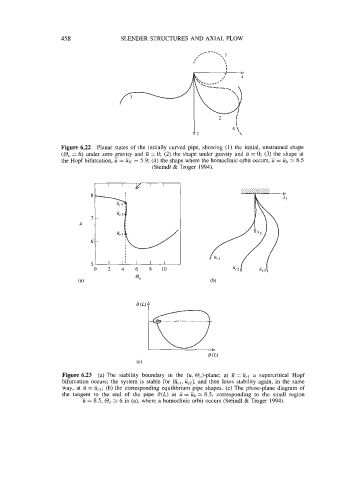
458 SLENDER STRUCTURES AND AXIAL FLOW
,,e------ .. 1
/
I \
I I
Figure 6.22 Planar states of the initially curved pipe, showing (1) the initial, unstrained shape
(0, = 6) under zero gravity and ii = 0; (2) the shape under gravity and U = 0; (3) the shape at
the Hopf bifurcation, U = U, = 5.9; (4) the shape where the homoclinic orbit occurs, E = iih 8.5
(Steindl & Troger 1994).
Figure 6.23 (a) The stability boundary in the (u, @,)-plane; at ii = Ucl a supercritical Hopf
bifurcation occurs; the system is stable for [Ec,, iic2], and then loses stability again, in the same
way, at ti = Ecj; (b) the corresponding equilibrium pipe shapes. (c) The phase-plane diagram of
the tangent to the end of the pipe B(L) at E = iih rx 8.5, corresponding to the small region
-
u = 8.5, 0, 2: 6 in (a), where a homoclinic orbit occurs (Steindl & Troger 1994).