Page 117 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 117
FLOW MEASUREMENT
94
4.1.8 Miscellaneous Types of Flow Meters
4.1.8.1 Target Flow Meters
. What are target meters? How do they work? What is
their plus point?
& In a target meter, a sharp-edged disk is set at right
angles to direction of flow and drag force exerted on
the disk by the fluid is measured.
& Figure 4.37 illustrates a target flow meter.
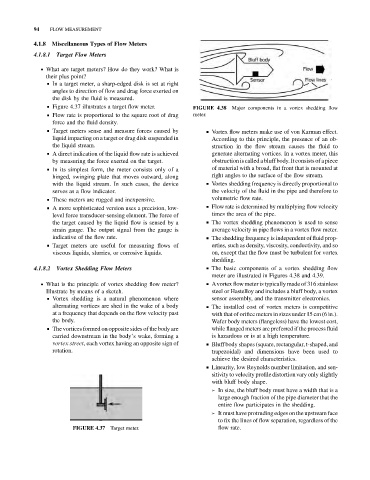
FIGURE 4.38 Major components in a vortex shedding flow
& Flow rate is proportional to the square root of drag meter.
force and the fluid density.
& Target meters sense and measure forces caused by & Vortex flow meters make use of von Karman effect.
liquid impacting on a target or drag disk suspended in According to this principle, the presence of an ob-
the liquid stream. struction in the flow stream causes the fluid to
& A direct indication of the liquid flow rate is achieved generate alternating vortices. In a vortex meter, this
by measuring the force exerted on the target. obstruction is called abluff body. It consists of apiece
& In its simplest form, the meter consists only of a of material with a broad, flat front that is mounted at
hinged, swinging plate that moves outward, along right angles to the surface of the flow stream.
with the liquid stream. In such cases, the device & Vortex shedding frequency is directly proportional to
serves as a flow indicator. the velocity of the fluid in the pipe and therefore to
& These meters are rugged and inexpensive. volumetric flow rate.
& Flow rate is determined by multiplying flow velocity
& A more sophisticated version uses a precision, low-
level force transducer-sensing element. The force of times the area of the pipe.
the target caused by the liquid flow is sensed by a & The vortex shedding phenomenon is used to sense
strain gauge. The output signal from the gauge is average velocity in pipe flows in a vortex flow meter.
indicative of the flow rate. & The shedding frequency is independent of fluid prop-
& Target meters are useful for measuring flows of erties, such as density, viscosity, conductivity, and so
viscous liquids, slurries, or corrosive liquids. on, except that the flow must be turbulent for vortex
shedding.
4.1.8.2 Vortex Shedding Flow Meters & The basic components of a vortex shedding flow
meter are illustrated in Figures 4.38 and 4.39.
. What is the principle of vortex shedding flow meter? & Avortex flow meter is typically made of 316 stainless
Illustrate by means of a sketch. steel or Hastelloy and includes a bluff body, a vortex
& Vortex shedding is a natural phenomenon where sensor assembly, and the transmitter electronics.
alternating vortices are shed in the wake of a body & The installed cost of vortex meters is competitive
at a frequency that depends on the flow velocity past with that of orifice meters in sizes under 15 cm (6 in.).
the body. Wafer body meters (flangeless) have the lowest cost,
& The vortices formed on opposite sides of the body are while flanged meters are preferred if the process fluid
carried downstream in the body’s wake, forming a is hazardous or is at a high temperature.
vortex street, each vortex having an opposite sign of & Bluff body shapes (square, rectangular, t-shaped, and
rotation. trapezoidal) and dimensions have been used to
achieve the desired characteristics.
& Linearity, low Reynolds number limitation, and sen-
sitivity to velocity profile distortionvary only slightly
with bluff body shape.
➢ In size, the bluff body must have a width that is a
large enough fraction of the pipe diameter that the
entire flow participates in the shedding.
➢ It must have protruding edges on the upstream face
to fix the lines of flow separation, regardless of the
Target meter. flow rate.
FIGURE 4.37