Page 115 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 115
FLOW MEASUREMENT
92
multiple pistons or pulsation dampening reservoirs & These applications involve accurate measurement
are installed. of volumetric flow ratios to be maintained
& Because of the close tolerances of the piston and between the process liquid volume and the chemical
cylinder sleeve, a flushing mechanism must be pro- injection volume. Examples include injection, or
vided in abrasive applications. introduction, of
& Piston pumps are sized on the basis of the displace- ➢ Sodium hypochlorite disinfectant into water.
ment of the piston and the required flow rate and ➢ Fertilizer into irrigation water.
discharge pressure. ➢ Bioengineered organisms into liquids for manu-
& Check valves (or, on critical applications, double facturing products such as soaps for large laun-
check valves) are selected to protect against reverse dries, defoaming chemicals, and insecticides.
flow. . What is an oval gear flow meter? What are its
& Diaphragm pumps are the most common industrial applications?
PD pumps. A typical configuration consists of a & An oval gear flow meter consists of two oval-shaped,
single diaphragm, a chamber, and suction and dis- fine-toothed gear rotors, one mounted vertically and
charge check valves to prevent reverse flow. the other horizontally, with gears meshing at the tip of
& The piston can either be directly coupled to the the vertical gear and the center of horizontal gear that
diaphragm or can force a hydraulic oil to drive the rotate within a chamber of specified geometry.
diaphragm. & The two rotors rotate opposite to each other, creating
& Maximum output pressure is about 8.6 barg an entrapment in the crescent-shaped gap between
(125 psig). the housing and the gear.
& Variations include bellows type diaphragms, hydrau- & As these rotors turn, they sweep out and trap a very
lically actuated double diaphragms, and air operated, precise volume of fluid between the outer oval shape
reciprocating double diaphragms. of thegears and the inner chamber walls, with none of
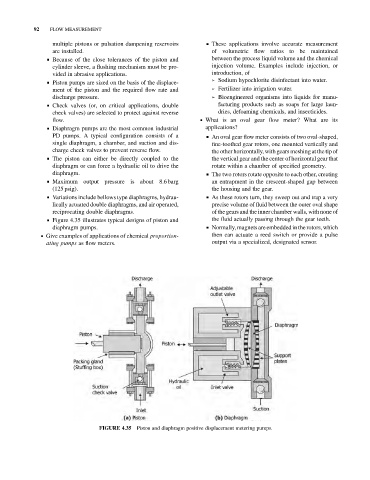
& Figure 4.35 illustrates typical designs of piston and the fluid actually passing through the gear teeth.
diaphragm pumps. & Normally, magnets are embedded in the rotors, which
. Give examples of applications of chemical proportion- then can actuate a reed switch or provide a pulse
ating pumps as flow meters. output via a specialized, designated sensor.
Piston and diaphragm positive displacement metering pumps.
FIGURE 4.35