Page 80 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 80
VALVES 57
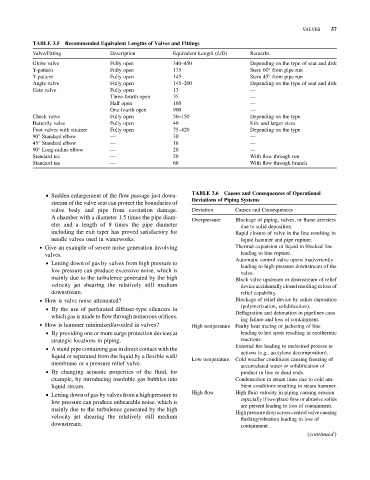
TABLE 3.5 Recommended Equivalent Lengths of Valves and Fittings
Valve/Fitting Description Equivalent Length (L/D) Remarks
Globe valve Fully open 340–450 Depending on the type of seat and disk
Y-pattern Fully open 175 Stem 60 from pipe run
Y-pattern Fully open 145 Stem 45 from pipe run
Angle valve Fully open 145–200 Depending on the type of seat and disk
Gate valve Fully open 13 —
Three-fourth open 35 —
Half open 160 —
One-fourth open 900 —
Check valve Fully open 50–150 Depending on the type
Butterfly valve Fully open 40 8 in. and larger sizes
Foot valves with strainer Fully open 75–420 Depending on the type
90 Standard elbow — 30 —
45 Standard elbow — 16 —
90 Long-radius elbow — 20 —
Standard tee — 20 With flow through run
Standard tee — 60 With flow through branch
& Sudden enlargement of the flow passage just down- TABLE 3.6 Causes and Consequences of Operational
stream of the valve seat can protect the boundaries of Deviations of Piping Systems
valve body and pipe from cavitation damage. Deviation Causes and Consequences
A chamber with a diameter 1.5 times the pipe diam-
Overpressure Blockage of piping, valves, or flame arresters
eter and a length of 8 times the pipe diameter due to solid deposition.
including the exit taper has proved satisfactory for Rapid closure of valve in the line resulting in
needle valves used in waterworks. liquid hammer and pipe rupture.
. Give an example of severe noise generation involving Thermal expansion of liquid in blocked line
valves. leading to line rupture.
Automatic control valve opens inadvertently
& Letting down of gas by valves from high pressure to
leading to high-pressure downstream of the
low pressure can produce excessive noise, which is
valve.
mainly due to the turbulence generated by the high Block valve upstream or downstream of relief
velocity jet shearing the relatively still medium device accidentally closed resulting in loss of
downstream. relief capability.
. How is valve noise attenuated? Blockage of relief device by solids deposition
(polymerization, solidification).
& By the use of perforated diffuser-type silencers in
Deflagration and detonation in pipelines caus
which gas is made to flow through numerous orifices.
ing failure and loss of containment.
. How is hammer minimized/avoided in valves? High temperature Faulty heat tracing or jacketing of line
& By providing one or more surge protection devices at leading to hot spots resulting in exothermic
strategic locations in piping. reactions.
External fire leading to undesired process re
& A stand pipe containing gas in direct contact with the
actions (e.g., acetylene decomposition).
liquid or separated from the liquid by a flexible wall/
Low temperature Cold weather conditions causing freezing of
membrane or a pressure relief valve.
accumulated water or solidification of
& By changing acoustic properties of the fluid, for product in line or dead ends.
example, by introducing insoluble gas bubbles into Condensation in steam lines due to cold am-
liquid stream. bient conditions resulting in steam hammer.
High flow High fluid velocity in piping causing erosion
& Letting down of gas by valves from a high pressure to
especially if two phase flow or abrasive solids
low pressure can produce unbearable noise, which is
are present leading to loss of containment.
mainly due to the turbulence generated by the high
High pressure drop across control valve causing
velocity jet shearing the relatively still medium
flashing/vibration leading to loss of
downstream. containment.
(continued )