Page 102 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 102
Be st Practice 2 .19 Pump Best Practices
Best Practice 2.19Practice 2.19Practice 2.19
Best
Best
Monitor parallel centrifugal pump operation by the use of Lessons Learned
manual or automatic differential pipe temperature to pre- Centrifugal pumps operating in parallel are prone to
vent parallel pump failure. damage from liquid vaporization when one or more pumps
Pumps that operate in parallel are subject to significant component have deficient head/flow curves resulting from internal
damage if they are not individually protected against minimum flow e component wear.
and usually they are not.
It has been my experience that most parallel pump systems are not
When pumps operate in parallel, the pump with the lowest head
monitored for individual reduced pump flow, and are not provided with
produced (worn pump and/or pump operating at the lowest speed) will
individual pump minimum flow protection. As a result, significant pump
be forced to reduced flow.
components can and will occur when one or more pumps have internal
Typically, for cost saving reasons, the minimum flow protection for
wear or operate at a reduced speed compared to the other pumps.
the pumps is installed in the pump discharge header and therefore
does not provide individual pump protection. Benchmarks
As the flow to any centrifugal pump decreases (see supporting
material below), the pump efficiency reduces and approaches 0% at This monitoring approach has been used since the mid-1990s to
ensure parallel pump optimum safety and reliability (MTBFs greater
zero flow. As a result, the pump differential temperature, which is close than 80 months).
to zero degrees Celsius in the safe operating region of flow, will in-
crease significantly as pump flow decreases.
Monitoring pump differential temperature is therefore a practical
way of determining parallel pump internal condition and speed (if the
pump driver is a variable speed type).
B. P. 2.19. Supporting Material A reduction in pump efficiency will result in an increase in
pump fluid differential temperature, which can be measured by
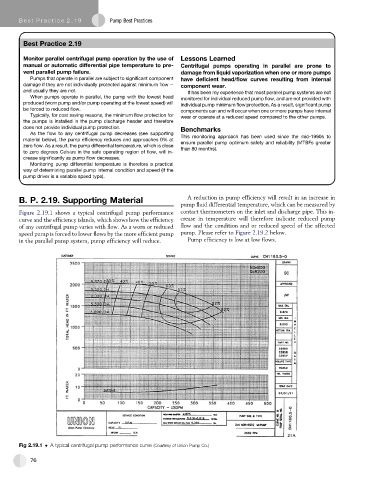
Figure 2.19.1 shows a typical centrifugal pump performance contact thermometers on the inlet and discharge pipe. This in-
curve and the efficiency islands, which shows how the efficiency crease in temperature will therefore indicate reduced pump
of any centrifugal pump varies with flow. As a worn or reduced flow and the condition and or reduced speed of the affected
speed pump is forced to lower flows by the more efficient pump pump. Please refer to Figure 2.19.2 below.
in the parallel pump system, pump efficiency will reduce. Pump efficiency is low at low flows.
Fig 2.19.1 A typical centrifugal pump performance curve (Courtesy of Union Pump Co.)
76