Page 393 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 393
Be st Practice 7 .7 Lube, Seal and Control Oil System Best Practices
prevent oil from entering the compressor case. The sizing of compressor, but too high a velocity could cause oil to enter
the orifice in the vent line of each drainer is critical, since it the compressor via the vent or reference line. Typical
ensures that all contaminated oil flow will enter the drainer. velocities in this line should be 4.6e6m/sec (15e20 ft/
Too low a velocity will allow contaminated oil to enter the sec).
Best Practice 7.7Practice 7.7
Best
Use centrifugal single stage pumps instead of screw Lessons Learned
pumps whenever possible, to increase the reliability of lube The most common cause of oil system induced unit trips is
oil systems. the failure of the backpressure control valve to respond to
The use of centrifugal pumps eliminates the need for relief and transient system changes (trip or slow speed reduction of
backpressure (bypass) control valves. the main turbine driven oil pump). The use of centrifugal
Malfunction of relief valves and/or backpressure control can cause
pumps eliminates the need for a backpressure control
an unscheduled shutdown of unit and hence result in significant rev-
valve.
enue loss.
Single stage centrifugal pumps can be used whenever the ambient
temperature along with the use of thermostatically controlled reservoir Benchmarks
heaters maintain an oil viscosity that allows the use of a centrifugal This best practice has been used since the mid-1980s to optimize the
pump (oil viscosity is low enough to minimize the effect of viscosity on reliability of oil systems, and to achieve compressor train reliabilities
centrifugal pump power e low viscosity correction factors). exceeding 99.7%
B.P. 7.7. Supporting Material
The pumps
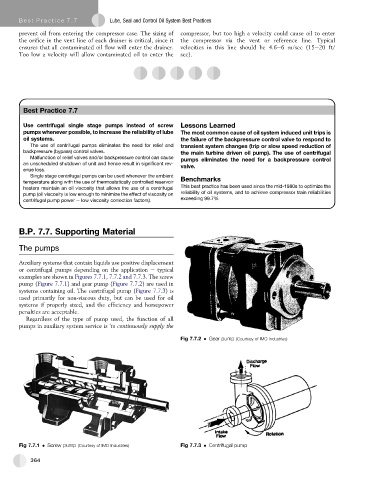
Auxiliary systems that contain liquids use positive displacement
or centrifugal pumps depending on the application e typical
examples are shown in Figures 7.7.1, 7.7.2 and 7.7.3. The screw
pump (Figure 7.7.1) and gear pump (Figure 7.7.2) are used in
systems containing oil. The centrifugal pump (Figure 7.7.3)is
used primarily for non-viscous duty, but can be used for oil
systems if properly sized, and the efficiency and horsepower
penalties are acceptable.
Regardless of the type of pump used, the function of all
pumps in auxiliary system service is ‘to continuously supply the
Fig 7.7.2 Gear pump (Courtesy of IMO Industries)
Fig 7.7.1 Screw pump (Courtesy of IMO Industries) Fig 7.7.3 Centrifugal pump
364