Page 363 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 363
1656_C007.fm Page 343 Monday, May 23, 2005 5:54 PM
Fracture Toughness Testing of Metals 343
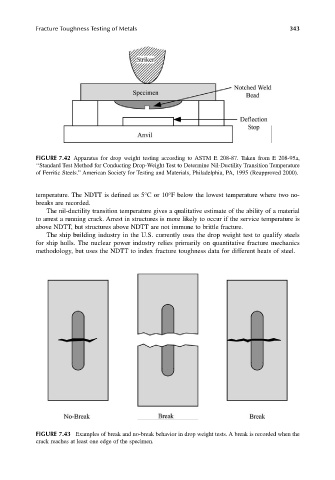
FIGURE 7.42 Apparatus for drop weight testing according to ASTM E 208-87. Taken from E 208-95a,
‘‘Standard Test Method for Conducting Drop-Weight Test to Determine Nil-Ductility Transition Temperature
of Ferritic Steels.’’ American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1995 (Reapproved 2000).
temperature. The NDTT is defined as 5°C or 10°F below the lowest temperature where two no-
breaks are recorded.
The nil-ductility transition temperature gives a qualitative estimate of the ability of a material
to arrest a running crack. Arrest in structures is more likely to occur if the service temperature is
above NDTT, but structures above NDTT are not immune to brittle fracture.
The ship building industry in the U.S. currently uses the drop weight test to qualify steels
for ship hulls. The nuclear power industry relies primarily on quantitative fracture mechanics
methodology, but uses the NDTT to index fracture toughness data for different heats of steel.
FIGURE 7.43 Examples of break and no-break behavior in drop weight tests. A break is recorded when the
crack reaches at least one edge of the specimen.