Page 107 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 107
92 From smart grid to internet of energy
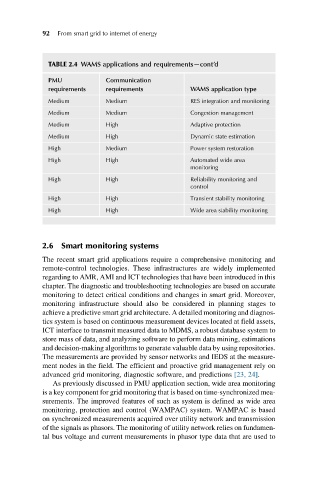
TABLE 2.4 WAMS applications and requirements—cont’d
PMU Communication
requirements requirements WAMS application type
Medium Medium RES integration and monitoring
Medium Medium Congestion management
Medium High Adaptive protection
Medium High Dynamic state estimation
High Medium Power system restoration
High High Automated wide area
monitoring
High High Reliability monitoring and
control
High High Transient stability monitoring
High High Wide area stability monitoring
2.6 Smart monitoring systems
The recent smart grid applications require a comprehensive monitoring and
remote-control technologies. These infrastructures are widely implemented
regarding to AMR, AMI and ICT technologies that have been introduced in this
chapter. The diagnostic and troubleshooting technologies are based on accurate
monitoring to detect critical conditions and changes in smart grid. Moreover,
monitoring infrastructure should also be considered in planning stages to
achieve a predictive smart grid architecture. A detailed monitoring and diagnos-
tics system is based on continuous measurement devices located at field assets,
ICT interface to transmit measured data to MDMS, a robust database system to
store mass of data, and analyzing software to perform data mining, estimations
and decision-making algorithms to generate valuable data by using repositories.
The measurements are provided by sensor networks and IEDS at the measure-
ment nodes in the field. The efficient and proactive grid management rely on
advanced grid monitoring, diagnostic software, and predictions [23, 24].
As previously discussed in PMU application section, wide area monitoring
is a key component for grid monitoring that is based on time-synchronized mea-
surements. The improved features of such as system is defined as wide area
monitoring, protection and control (WAMPAC) system. WAMPAC is based
on synchronized measurements acquired over utility network and transmission
of the signals as phasors. The monitoring of utility network relies on fundamen-
tal bus voltage and current measurements in phasor type data that are used to