Page 297 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 297
264 From smart grid to internet of energy
management systems cause to several concerns about consumer’s privacy,
decentralized managements systems have been proposed for privacy protection.
There several DR control methods are improved where widely accepted three
types are ToU, real time pricing, and critical pricing. A variety of researches and
several home energy management systems have been proposed in the context of
MAS, a multi-objective mixed integer nonlinear programming (MO-MINLP)
model, and mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) by considering the
DERs and load profiles of consumers. A significant control system at the con-
sumption level is microgrid controller that manages the PQ of the generated
energy by consumers. The controlled microgrid can be one of residential, com-
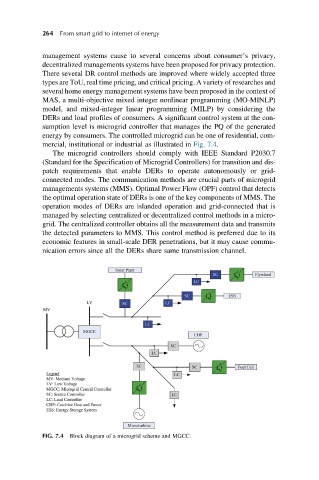
mercial, institutional or industrial as illustrated in Fig. 7.4.
The microgrid controllers should comply with IEEE Standard P2030.7
(Standard for the Specification of Microgrid Controllers) for transition and dis-
patch requirements that enable DERs to operate autonomously or grid-
connected modes. The communication methods are crucial parts of microgrid
managements systems (MMS). Optimal Power Flow (OPF) control that detects
the optimal operation state of DERs is one of the key components of MMS. The
operation modes of DERs are islanded operation and grid-connected that is
managed by selecting centralized or decentralized control methods in a micro-
grid. The centralized controller obtains all the measurement data and transmits
the detected parameters to MMS. This control method is preferred due to its
economic features in small-scale DER penetrations, but it may cause commu-
nication errors since all the DERs share same transmission channel.
FIG. 7.4 Block diagram of a microgrid scheme and MGCC.