Page 162 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 162
5.2 Chapter Five
1.5
1
0.5
m(t) 0
−0.5
−1
−1.5
0 5 10 15 20
Time, t, sec
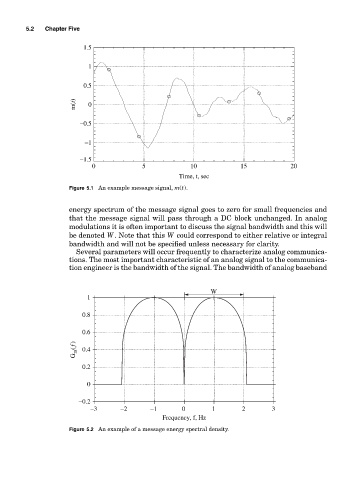
Figure 5.1 An example message signal, m(t).
energy spectrum of the message signal goes to zero for small frequencies and
that the message signal will pass through a DC block unchanged. In analog
modulations it is often important to discuss the signal bandwidth and this will
be denoted W. Note that this W could correspond to either relative or integral
bandwidth and will not be specified unless necessary for clarity.
Several parameters will occur frequently to characterize analog communica-
tions. The most important characteristic of an analog signal to the communica-
tion engineer is the bandwidth of the signal. The bandwidth of analog baseband
W
1
0.8
0.6
G m ( f ) 0.4
0.2
0
−0.2
−3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3
Frequency, f, Hz
Figure 5.2 An example of a message energy spectral density.