Page 164 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 164
5.4 Chapter Five
0.3 −30
−35
0.2
−40
0.1 −45
−50
0
m(t) G m (f), dB −55
−0.1 −60
−0.2 −65
−70
−0.3
−75
−0.4 −80
0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03 0.035 0.04 0.045 0.05 −2 −1.5 −1 −0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2
Time, t, sec Frequency, f, Hz × 10 4
(a) Time waveform (b) Power spectrum
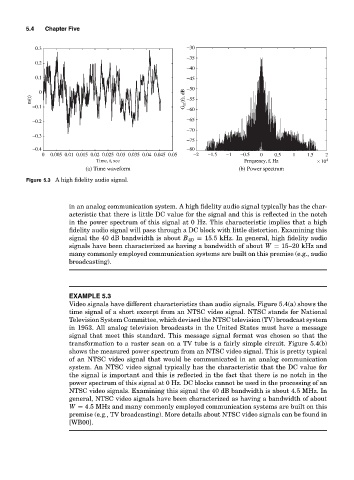
Figure 5.3 A high fidelity audio signal.
in an analog communication system. A high fidelity audio signal typically has the char-
acteristic that there is little DC value for the signal and this is reflected in the notch
in the power spectrum of this signal at 0 Hz. This characteristic implies that a high
fidelity audio signal will pass through a DC block with little distortion. Examining this
signal the 40 dB bandwidth is about B 40 = 15.5 kHz. In general, high fidelity audio
signals have been characterized as having a bandwidth of about W = 15–20 kHz and
many commonly employed communication systems are built on this premise (e.g., audio
broadcasting).
EXAMPLE 5.3
Video signals have different characteristics than audio signals. Figure 5.4(a) shows the
time signal of a short excerpt from an NTSC video signal. NTSC stands for National
Television System Committee, which devised the NTSC television (TV) broadcast system
in 1953. All analog television broadcasts in the United States must have a message
signal that meet this standard. This message signal format was chosen so that the
transformation to a raster scan on a TV tube is a fairly simple circuit. Figure 5.4(b)
shows the measured power spectrum from an NTSC video signal. This is pretty typical
of an NTSC video signal that would be communicated in an analog communication
system. An NTSC video signal typically has the characteristic that the DC value for
the signal is important and this is reflected in the fact that there is no notch in the
power spectrum of this signal at 0 Hz. DC blocks cannot be used in the processing of an
NTSC video signals. Examining this signal the 40 dB bandwidth is about 4.5 MHz. In
general, NTSC video signals have been characterized as having a bandwidth of about
W = 4.5 MHz and many commonly employed communication systems are built on this
premise (e.g., TV broadcasting). More details about NTSC video signals can be found in
[WB00].