Page 179 - Fundamentals of Computational Geoscience Numerical Methods and Algorithms
P. 179
7.3 Verification and Application of the Equivalent Source Algorithm 169
9
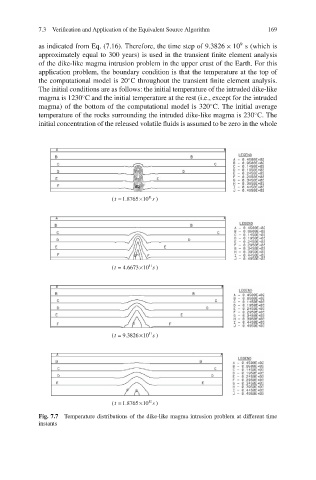
as indicated from Eq. (7.16). Therefore, the time step of 9.3826 × 10 s(whichis
approximately equal to 300 years) is used in the transient finite element analysis
of the dike-like magma intrusion problem in the upper crust of the Earth. For this
application problem, the boundary condition is that the temperature at the top of
◦
the computational model is 20 C throughout the transient finite element analysis.
The initial conditions are as follows: the initial temperature of the intruded dike-like
◦
magma is 1230 C and the initial temperature at the rest (i.e., except for the intruded
magma) of the bottom of the computational model is 320 C. The initial average
◦
◦
temperature of the rocks surrounding the intruded dike-like magma is 230 C. The
initial concentration of the released volatile fluids is assumed to be zero in the whole
(t = . 1 8765 × 10 11 s )
(t = . 4 6673× 10 11 s )
(t = . 9 3826 × 10 11 s )
(t = . 1 8765 × 10 12 s )
Fig. 7.7 Temperature distributions of the dike-like magma intrusion problem at different time
instants